Standard rigid FR4 boards offering stable structure for general electronic systems.
- - Strong mechanical support and heat resistance
- - Supports complex, high‑density layouts
- - Easy for automated assembly
- - Widely used across industries
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
Metal-Core PCBs (MCPCBs) are renowned for their exceptional thermal management and durability, making them ideal for high-power applications. Among the available options, aluminum-based PCBs are the most popular due to their lightweight design, cost-effectiveness, and excellent heat dissipation. Whether you're working on LED lighting, power electronics, or automotive applications, aluminum-backed PCBs can significantly enhance performance while keeping costs low.
NextPCB offers a range of metal-core PCB manufacturing services, including aluminum, copper, iron and stainless steel PCB manufacture with support for pedestal designs, counterbore/countersunk holes, z-axis milling, blind vias and more.
Aluminum PCBs are a type of metal-core printed circuit board (MCPCB) that uses solid aluminum metal for its base. The lightweight metal gives aluminum PCBs heat dissipation properties magnitudes higher than conventional fibreglass FR4 PCBs without the weight and bulkiness of copper-backed PCBs.
Aluminum PCBs and other PCBs using metal substrates have the typical structure as shown below.
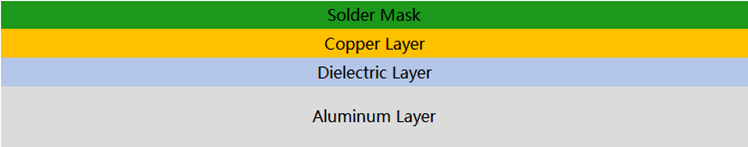
A thin dielectric layer is sandwiched between the traces on one side and the metal base on the other. The dielectric layer, often made of FR4, ceramic or polymer, is thermally conductive but electrically insulating, and serves the purpose of dividing the two metallic layers while allowing as much heat transfer as possible. As such, metal-core PCBs are also referred to as insulated metal substrates (IMS).
Single-sided, single-layer aluminum PCBs are the most common as the aluminum base occupies an entire side of the PCBs, limiting their complexity. Although multilayer and double-sided aluminum PCBs are possible by stacking layers on one side and using insulated interconnects, the additional insulating layers act as another thermal barrier, severely disrupting the PCB's overall ability to disperse heat. These structures are also significantly more complex, requiring additional processes and technology, which increases costs considerably.
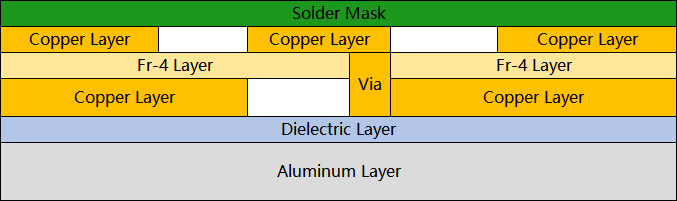
Single-sided two-layer (multilayer) aluminum PCB
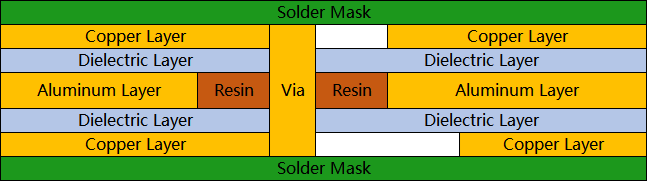
Double-sided two-layer aluminum PCB. Notice the walls of the via are insulated with resin to prevent short circuits through the aluminum base.
Since aluminum PCBs are popular in lighting applications such as high-power LED PCBs, they are commonly paired with white solder mask to enhance reflectivity and light uniformity. NextPCB also has high reflectivity white, black and matte black solder mask options for various lighting effects.
As with other metal-core PCBs, the primary advantage of these structures is the high thermal conductivities of the base metals. Aluminum metal has a thermal conductivity of around 150W/mK, and although the presence of the dielectric barrier brings this down to around 1-5W/mk, this is still 10-20 times greater than typical FR4 circuit boards.
Aluminum-core PCBs are relatively lightweight, with aluminum metal having just a third of the weight of copper, another commonly used IMS metal. This makes aluminum ideal for weight-sensitive applications such as portable electronics, mounted lighting, automotive and aerospace applications.
Single-layer aluminum PCBs are relatively inexpensive due to aluminum’s abundance and relatively simple processing. On the other hand, copper core and ceramic PCBs have higher material and processing costs.
As a metal, aluminum is highly durable and offers extra rigidity and strength to the PCB compared to fiberglass epoxy substrates. At lower thicknesses, the ductile nature of metals also allows for bendable electronics such as bendable LED strips or sub-flex rigid-flex structures, achieved by removing material in bend areas.
Aluminum’s light weight and durability also make larger PCBs viable in many applications. The maximum dimensions for NextPCB’s aluminum PCBs are 1200 x 540 mm. Compare this to ceramic PCBs, which, due to their brittleness, have maximum dimensions of only 120 x 120mm. This makes aluminum a great choice for large LED panels and displays.
The metallic substrate acts as an EMI shield, improving signal integrity in high-frequency circuits.
Aluminum-core circuit boards' key advantages are their thermal management properties, light weight and cost, making them ideal for high-power LED lighting applications, consumer power electronics and cost-sensitive thermal applications.
For higher power applications requiring greater thermal conductivities, aluminum PCBs fall short. While pedestal technology can bypass the dielectric barrier to improve heat transfer, machining aluminum for this purpose is expensive and challenging due to its lower hardness.
Copper pedestals are easier to form due to the metal’s higher hardness. Combined with copper’s higher thermal conductivity (400W/mK), copper-core PCBs may be a much more viable option for high-power electronics compared to aluminum.
For applications requiring high thermal conductivity, tighter circuit density and lightweight properties, ceramic PCBs are also a consideration but at a significantly higher cost compared to aluminum PCBs.
Unlike fiberglass PCBs, metal-core (Al/Cu) and ceramic PCBs have limited circuit density, restricting them to simpler designs in most cases. Nor can they compare in terms of the flexibility, low cost and versatility of conventional fiberglass PCBs.
>> Recommeng reading: Ceramic PCB vs FR4 vs Metal-Core: Substrates for Thermal Management
Consider aluminum core PCBs for simple, cost-sensitive applications requiring moderate thermal management, durability and light weight.

For reliable, high-quality aluminum PCBs at competitive prices, trust NextPCB. NextPCB supports a wide range of aluminum and copper substrates for metal-core PCBs for any occasion. Get an online quote or contact us for customized solutions fit for your needs.
| Specification | Capability |
|---|---|
| Structure | Single-sided, double-sided, multilayer base and more |
| Material Brands | Ventec, Shengyi, Totking and Boyu See below for more information |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1 to 5 W/mk |
| Max Dimensions | 1200 x 540 mm |
| Board Thickness | 0.4 to 3.0 mm |
| Copper Weight | 0.5 to 4 oz (140 μm) |
| Min. Trace Width/Spacing | 4/4 mil |
| Drill and Via Capabilities |
|
| Min. Hole Size | 0.3 mm |
| Surface Finish | HASL, Lead free HASL, ENIG, OSP |
| Solder Mask | Green, White, High Reflectivity White, Black, Matte Black |
| Extras | Pedestal technology |
| Industries & Applications |
|
Please inquire for advanced capabilities.
Below are some of the most common metal-core materials we support. Contact us for more information and other materials, including stainless steel and iron.
| Material Code | Brand | Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
Tg (℃) | Data Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VT-4A2H | Ventec | Aluminum | 2.2 | 105 | VT-4A2H.pdf |
| VT-4B3 | Ventec | Aluminum | 3.0 | 130 | VT-4B3.pdf |
| VT-4B5 | Ventec | Aluminum | 4.2 | 130 | VT-4B5.pdf |
| SAR15 | Shengyi | Aluminum | 1.5 | 140 | SAR15.pdf |
| SAR10S | Shengyi | Aluminum | 1.1 | 140 | SAR10S.pdf |
| SAR20H | Shengyi | Aluminum | 2.2 | 160 | SAR20H.pdf |
| SCR20S | Shengyi | Copper | 2.1 | 160 | SCR20S.pdf |
| T110 | Totking | Aluminum | 1.5 | 100 | T110.pdf |
| T111 | Totking | Aluminum | 2.0 | 100 | T111.pdf |
| T112 | Totking | Aluminum | 3.0 | 100 | T112.pdf |
| T112B | Totking | Aluminum | 4.0 | 130 | T112B.pdf |
| T112C | Totking | Aluminum | 5.0 | 155 | T112C.pdf |
| T511 | Totking | Copper | 3.0 | 100 | T511.pdf |
| T512 | Totking | Copper | 4.0 | 100 | T512.pdf |
| T512C | Totking | Copper | 5.0 | 130 | T512C.pdf |
| AL-01-B10 | Boyu | Aluminum | 1.0 | 110 | AL-01-B10.pdf |
| AL-01-B20 | Boyu | Aluminum | 2.0 | 130 | AL-01-B20.pdf |
| AL-01-B30L | Boyu | Aluminum | 3.0 | 130 | AL-01-B30L.pdf |
PCB is the abbreviation of the...