Introduction
V-Cut, also known as V-Scoring or V-Grooving, is a core technique in the Printed Circuit Board manufacturing (PCB) and Electronics Assembly (PCBA) processes for achieving efficient depaneling (separation). For professionals involved in electronic design, hardware engineering, PCB procurement, or SMT production, understanding the working principle, parameter control, and impact of V-Scoring on edge stress is crucial.
This method significantly reduces the local thickness of the material by creating precise V-shaped grooves on the panelized PCB, providing an ideal weakened line for subsequent mechanical separation. It is particularly suitable for high-volume PCB production that requires high-efficiency, low-cost straight-line segmentation.
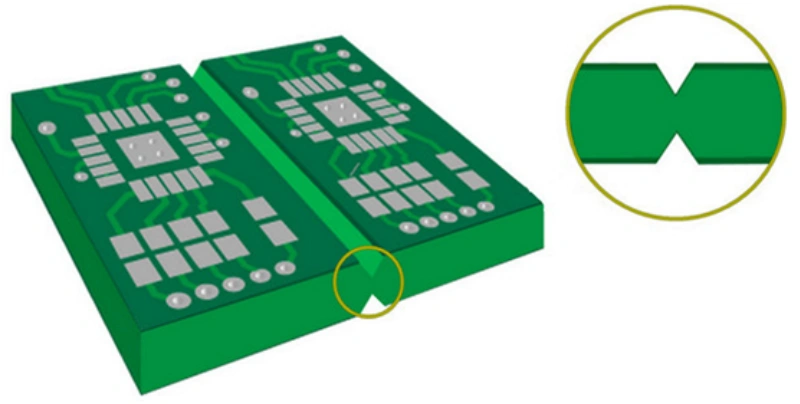
What is V-Scoring?
V-Scoring involves cutting a V-shaped groove into both the top and bottom surfaces of the PCB. These two grooves are typically positioned directly opposite each other at a predetermined depth. The resulting V-shaped channels drastically reduce the board material's thickness at this point, creating a weak spot that facilitates subsequent physical separation.
Primary Uses of V-Scoring
The core function of V-Scoring is to improve depaneling efficiency and quality. It is primarily used for:
-
Panel Separation: In PCB fabrication, multiple identical or different designs are often arrayed on a larger substrate (known as a panel or panelized PCB) to maximize production efficiency. V-Scoring is used to mark and weaken the connection area between these individual boards.
-
Facilitating Mechanical Depaneling: Automated depaneling machines or manual operators can easily cut or snap the panel along these V-groove lines to separate it into individual boards.
Key Parameters and Principle
The implementation of V-Scoring requires precise control over several key parameters:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Residual Thickness (Web Thickness) |
The remaining thickness of the PCB material at the bottom of the V-groove after cutting. This is the most critical parameter, determining the ease of separation and the magnitude of edge stress. It is usually set to about 1/3 to 1/4 of the total board thickness. |
|
V-Groove Angle |
The opening angle of the V-groove. Common angles are 30∘, 45∘, or 60∘. A larger angle generally results in lower edge stress during separation. |
|
Positional Accuracy |
The precision of the V-groove line's placement on the PCB, which directly affects the final board size and quality after separation. |
Principle: V-Scoring utilizes the principle of stress concentration. By carving the V-grooves, the stress required for separation is concentrated at the thin, remaining web thickness. When an external force is applied (such as roller cutting or snapping), the board material breaks quickly and cleanly along the V-groove line.
Advantages and Disadvantages of V-Scoring
|
Aspect |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Efficiency & Cost |
Relatively low cost; fast depaneling speed; suitable for high-volume production. |
May generate significant mechanical stress during separation, making it unsuitable for components sensitive to stress (e.g., ceramic capacitors). |
|
Board Edge |
The separated board edge is typically straight. |
Cannot achieve non-linear separation; limited to straight-line cuts. The edge may have slight burrs or roughness. |
|
Space Utilization |
Compared to routing, it allows for smaller panel gaps, improving substrate utilization. |
Requires a keep-out area; no components, pads, or traces can be placed near the V-groove line. |
Comparison with Other Depaneling Methods
V-Scoring is most commonly compared with the Routing method:
- V-Scoring: Suitable for straight-line cuts; high efficiency and low cost, but high stress; cannot cut complex shapes.
- Routing: Uses a milling cutter for separation; suitable for complex or curved cuts; lower stress, but leaves connecting points (e.g., break-away tabs or mouse bites); slower depaneling time and higher cost.
Choose NextPCB for Manufacturing Your V-Scored PCBs
Now that you understand the advantages and technical requirements of V-Scoring, you need a manufacturer who can deliver high-precision V-grooving and strict quality control.
NextPCB possesses advanced V-Scoring equipment and extensive manufacturing experience, allowing for precise control over residual thickness and cutting angles, ensuring a smooth and reliable depaneling process for your panels.
Submit your design files today and experience our high-quality PCB manufacturing service! Whether you require V-Scoring for high-efficiency bulk orders or precision boards with strict mechanical stress limits, NextPCB can provide the professional solution you need.




