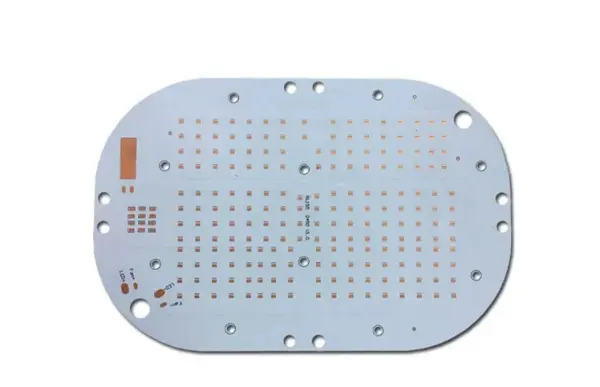
PCBs with aluminum metal core for efficient heat dissipation in high‑power designs.
- - Excellent thermal management and durability
- - Lightweight and cost‑effective
- - Good choice for LED/power electronics
- - Metallic core also helps EMI control
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the foundation of nearly all electronic devices, providing a structured platform for components to interconnect. Among the different types of PCBs, rigid PCBs are the most widely used due to their reliability, durability, and ease of mass production.
NextPCB offers a wide range of rigid PCB manufacturing services for any application, from FR4, metal-core to ceramic PCBs.
Rigid PCBs are traditional non-flexible circuit boards made from solid substrates, typically FR4 (fiberglass epoxy laminate), which provides mechanical stability for the circuitry and components.
Initially developed to replace cumbersome breadboard wiring, rigid PCBs can consist of a wide variety of materials and configurations, but they typically share the same structure: conductive layers for the circuitry (typically copper traces), insulating layers made of dielectric material that separate conductive layers, and solder mask and silkscreen - the protective covering and text/markings, respectively.
The non-flexible and sturdy nature of rigid PCBs secures components and copper patterns in place, minimizing damage from vibrations, shocks and bending.
The stability of rigid circuits allows for the construction of complex and precise structures, such as those made from fibreglass epoxy. Advanced techniques for creating blind/buried vias and fine traces work best with hard, static structures, allowing for intricate machining and processing.
Rigid PCBs are highly suited for machine processing, improving efficiency and reducing costs during assembly. The boards can be held in place in various machines or travel along conveyors without deformation or external mechanical support. The flat, stable surface is ideal for precise solder paste application and component placement.
The solid nature of rigid PCBs facilitates heat transfer and heat resistance. Metal-core PCBs using high-conductivity metals and ceramic PCBs are designed for effective thermal management for high-temperature applications.
Rigid PCBs have a wealth of advantages and strong points, however, there are applications where flexibility and non-rigid circuit boards are favourable. In such cases, flexible PCBs or rigid-flex PCBs can be considered.
Rigid versus Flexible PCBs table
NextPCB supports a wide variety of rigid PCB types for applications in consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial control, medical devices and more. Find out more below or contact us for more information.
PCB is the abbreviation of the...