
 PCB Assembly Factory Show
Certificate
PCB Assembly Factory Show
Certificate
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
Professional PCB Manufacturing Specifications and Process Standards
Cutting-edge technology meets precision manufacturing. Our comprehensive capabilities cover everything from simple single-layer boards to complex multilayer HDI designs.
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer count | 1 - 32 layers | Supports multilayer PCB manufacturing up to 32 layers, including advanced structures like 32L HDI/Rigid-Flex Support, suitable for high-density applications | / |
| Impedance | For 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 layers PCB, PCB Stackup designed by NextPCB(by default), or PCB Stackup designed by customers | Standard pcb design for manufacturing flow includes impedance calculation based on default or customer-provided stackups. Ideal for RF/high-speed signal applications. |
Layer Stackup Structure Impedance Calculation Parameter |
| Impedance tolerance | ±10% | Ensures signal integrity in impedance-controlled PCBs for high-frequency applications | / |
| Material | FR-4 | Multiple Tg options available: TG130 / TG150 / TG170. These material options enable flexible pcb prototype fabrication service from standard to high-performance needs |  |
| PCB material dielectric constant | 4.2 | Based on prepreg types: 7628 / 1080 / 2313 / 2116. Dielectric stability is critical for RF and signal-controlled PCB applications | / |
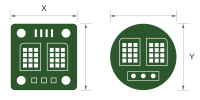
| Max. dimension |
1-2 layers: 1500*600mm 4 layers: 1500*500mm 6+layers: 500*400mm |
Reflects NextPCB capabilities for large-format board manufacturing |
|
| Min. dimension | ≥10×10mm | Suitable for small-format pcb prototype fabrication service, particularly useful in compact consumer electronics | / |
| Dimension tolerance | CNC: ±0.15mm, V-CUT: ±0.2mm |
Tight pcb tolerances ensure outline precision and reduce post-processing mismatch risk ±0.15mm for CNC routing, ±0.2mm for V-scoring |
/ |
| PCB thickness | 0.6/0.8/1.0/1.2/1.6/2.0/2.5/3.0/3.2mm | The thickness of finished board. This broad range meets standard and high-current carrying PCB applications. |
|
|
Thickness tolerance ( Thickness≥1.0mm) |
±10% |
Enables accurate pcb manufacturing capabilities for multilayer boards Example: If the board thickness is 1.6mm, the finished board thickness ranges from 1.44mm(1.6-1.6×10%) to 1.76mm(1.6+1.6×10%) |
/ |
|
Thickness tolerance ( Thickness < 1.0mm) |
±0.1mm |
Critical for thin board stackups in handhelds and flexible PCB applications Example: If the board thickness is 0.8mm, the finished board thickness ranges from 0.7mm(0.8-0.1) to 0.9mm(0.8+0.1) |
/ |
| Finished copper weight | 1 oz/2 oz |
Finished copper weight of outer layer could be 1 oz/2 oz 2oz copper thickness ensures high current capability and thermal performance in power boards" |
|
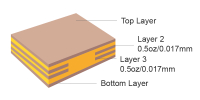
| Inner copper weight | 0.5 oz/1 oz/2 oz |
Finished copper weight of inner layer could be 0.5 oz/1 oz/2 oz Flexible copper distribution supports thermal design optimization and signal integrity |
|
| Surface finish | Multiple finishes to meet RoHS/REACH and solderability needs. Ideal for global PCB deployment | / | / |
| HDI structure | Rank 1 /Rank 2 /Rank 3 |
Advanced HDI options Mechanical blind buried vias or laser blind buried vias(electroplating Via-filling is available) or laser blind vias filling dimple ≤ 15µm Optimized for smartphones, wearables, and IoT boards" |
/ |
| Electrical test | Flying Probe/Special test fixture | No pad count limits on flying probe. Fixture-based test supports up to 14,000 pads. Enables strict quality assurance in pcb manufacturer China standard | / |
| Beveling angle of gold finger | 20°/30°/45°/60° | Available for edge connectors in industrial and consumer hardware | / |
| Beveling angle tolerance of gold finger | ±5° | Ensures reliable mechanical contact and insertion accuracy | / |
| Beveling depth tolerance of gold finger | ±0.1mm | Precision control benefits connector mating and assembly yield | / |
| Outline tolerance | ±0.15mm | Supports CNC routing and tight-fitting mechanical enclosures | / |
| V-CUT angle | 30°/45°/60° | Various depaneling options suitable for volume pcb prototype fabrication service | / |
| Number of V-CUT | ≤30 cuts | Efficient for panelized delivery and cost-effective volume processing | / |
| V-CUT outline size | 55mm ≤ length/width ≤ 480mm | Optimized for panelized batch manufacturing | / |
| V-CUT residue thickness | 0.25mm ≤ v-cut residue thickness ≤ 0.4mm | Balances structural integrity and ease of separation post-reflow | / |
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
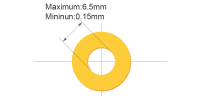
| Drill hole size(Mechanical) | 0.15-6.5mm |
Minimum drill hole size is 0.15 mm (available for PCB thickness ≤ 1.2 mm). Maximum drill
diameter is
6.5 mm. For custom holes beyond this range, contact support@nextpcb.com These specs reflect NextPCB’s pcb manufacturing capabilities in high-precision micro drilling. |
|
| Drill hole size tolerance | ≤0.05mm | Ensures high pcb tolerances for hole precision, suitable for dense BGA designs and controlled impedance boards | / |
| Blind/Buried vias | Mechanical blind buried vias: copper thickness of blind vias ≥ 20µm | Supports HDI designs with microvia stacking. Complies with HDI PCB and via aspect ratio standards for high-density interconnects. |
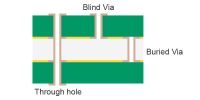
|
| Laser blind buried vias: dimple ≤ 10µm |
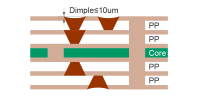
|
||
| Via pad size | ≥0.1mm | The pad hole size will be enlarged 0.125mm in production to compensate for plating buildup. Proper design is crucial for pcb design for manufacturing (DFM). |
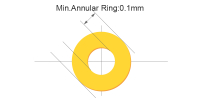
|
| PTH hole size | ≥0.2mm (for single side) | The annular ring size will be enlarged by 0.2mm in production to ensure plating quality and drill registration. Ideal for pcb prototype fabrication service and low-volume builds. |
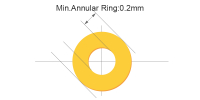
|
| Min. non-plated holes | ≥0.4mm | Used for mechanical fixture holes, thermal reliefs, or mounting pads. Not subject to plating-related variation. |
|
| Min. plated slots | ≥0.5mm | Ensures reliable plating within slotted areas for connectors or edge components. Properly designed plated slots reduce the risk of barrel cracking during reflow. |
|
| Min. non-plated slots | ≥0.5mm | Common for isolation cutouts and component clearance zones. Recommended to avoid mechanical stress cracking. |
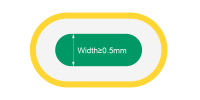
|
| Min. castellated holes | ≥0.5mm | Castellated holes (half-holes on board edges) are widely used for board-to-board soldering. NextPCB supports castellated features with minimum diameter of 0.5mm |
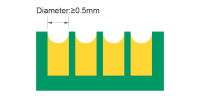
|
| Hole size tolerance(Plated) | ±0.075mm |
Example: If customed Plated hole size is 1.000mm, final size may range from 0.925mm to
1.075mm. Reflects tight pcb tolerances suitable for press-fit connectors. |
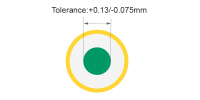
|
| Hole size Tolerance(Non-Plated) | ±0.05mm |
Example: If customed Non-Plated hole size is 1.000mm, final may range from 0.95mm to
1.05mm. Maintains mechanical dimension control for mounting hardware. |
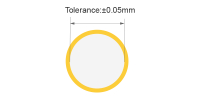
|
| Rectangle hole/Slot | With or without fillet angle | Supports rectangular or slotted holes with optional fillet angles. Useful for USB, HDMI, or edge connectors in pcb manufacturer China standards |

|
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 oz Copper | 3.5mil (single side) (3.5mil≈0.09mm) | This minimum annular ring is suitable for standard trace designs and via pads under regular current conditions. Reflects typical pcb tolerances used in most mid-density boards. |
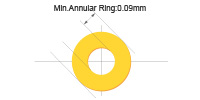
|
| 2 oz Copper | 4.5mil (single side) (4.5mil≈0.11mm) | Thicker copper requires a slightly larger annular ring to ensure sufficient plating coverage and mechanical strength. Complies with 2oz copper thickness industry standards for power applications. |
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hole to hole clearance(Different nets) | ≥12mil(Avoid conductive anodic filament)(12mil≈0.30mm) | Designed to prevent CAF (Conductive Anodic Filament) formation and electrical shorting between unrelated nets. Part of high-reliability pcb design for manufacturing considerations. |
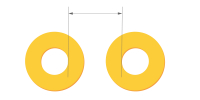
|
| Via to via clearance(Same nets) | ≥8mil (8mil≈0.20mm) | Optimized for dense via array routing while ensuring drill registration. Typical for high-speed, BGA breakout routing. |
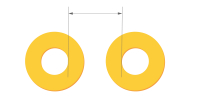
|
| SMD pad to SMD pad clearance(Pad without hole, different nets) | ≥0.15mm | Ensures solder mask coverage and prevents bridging. Crucial for fine-pitch QFP, QFN, or 0201 passive designs. |
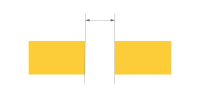
|
| Pad to pad clearance(Pad with hole, different nets) | ≥0.40mm | Allows sufficient annular ring and solder mask between plated through-holes of different networks. Supports pcb capabilities in multilayer designs. |
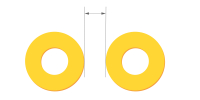
|
| Via to track | ≥7mil (7mil≈0.18mm) | Ensures trace isolation from plated through-via walls, especially in high aspect ratio PCBs. Minimizes etching defects. |
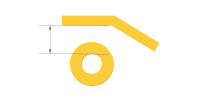
|
| PTH to track | ≥9mil (9mil≈0.23mm) | Used in high-current and multi-net routing where pcb tolerances and copper clearance are critical. |
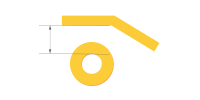
|
| NPTH to track | ≥8mil (8mil≈0.20mm) | Non-plated mounting or tooling holes require isolation to maintain mechanical and dielectric performance. |
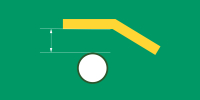
|
| SMD pad to track | ≥4mil (4mil≈0.10mm) | Ensures solder mask or air-gap between SMD pad and adjacent trace. Supports HDI and compact layout standards from pcb manufacturer China. |
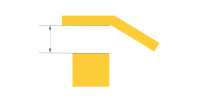
|
| Copper weight | Min. trace width | Min. spacing | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| H/HOZ(0.5oz Inner layer) | 2.5mil (2.5mil≈0.06mm) | 3mil (3mil≈0.08mm) |
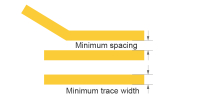
|
| 1 oz(Outer layer) | 3mil (3mil≈0.08mm) | 3mil (3mil≈0.08mm) | |
| 2 oz(Outer layer) | 5.5mil (5.5mil≈0.14mm) | 5.5mil (5.5mil≈0.14mm) |
| Layer count | Min. BGA pad dimensions | Min. distance between BGA | Min. spacing between the center of two BGAs | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 oz | ≥0.2mm | 0.15mm | 0.45mm | Satisfies mainstream BGA packaging requirements, including 0.5mm and 0.8mm pitch devices. Optimized for via-in-pad, dog-bone fanout and via aspect ratio balancing |
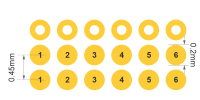
|
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solder mask opening/expansion | ≥1.5mil (1.5mil≈0.04mm) | A solder mask opening of at least 1.5mil around the pad is required to accommodate potential registration tolerances. This is a key aspect of pcb design for manufacturing, especially for fine-pitch SMDs. |
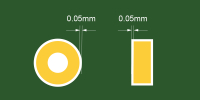
|
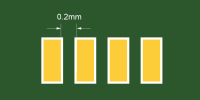
| Solder bridge |
Green: 3.5mil Black/White: 5mil other solder mask: 4mil |
To reliably form a solder bridge (mask dam), the edge-to-edge spacing between copper pads must meet or exceed the values listed. Green offers the best resolution, making it the most common solder mask choice in pcb prototype fabrication service. |
|
| Solder mask color | Green/Red/Yellow/Blue/White/ Matte Black/Black | Aesthetic and functional choice. Green offers the best visual contrast and process control. Matte finishes help reduce glare during AOI inspection. | / |
| Solder mask dielectric constant | 3.5 | Influences high-frequency signal performance and impedance control in controlled dielectric stackups. Relevant in HDI PCB and RF board design. | / |
| Solder mask thickness | Solder mask thickness on base material: 0.8mil, solder mask thickness on copper: 0.6mil | Uniform solder mask thickness is important to avoid solder mask slivers and to ensure adequate insulation between conductive areas. Controlled thickness enhances long-term environmental resistance. | / |
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum line width |
Silkscreen printing≥5mil (5mil≈0.12mm) Printer printing≥3mil (3mil≈0.08mm) |
Character strokes thinner than 3mil (0.076mm) may become blurred or unreadable. This specification is important for component marking clarity in pcb prototype fabrication service. |

|
| Minimum text height |
Silkscreen printing≥30mil
(30mil≈0.76mm)
Printer printing≥24mil (24mil≈0.61mm) |
Characters below 24mil in height may not be recognizable after solder mask and reflow. Following pcb design for manufacturing guidelines ensures legibility in assembly and testing. |

|
| Character width to height ratio | ≥ 6:1 | Ensures optimal aspect ratio for printed text readability. A 6:1 ratio minimizes distortion or "bleeding" during silkscreen curing and soldering processes. | / |
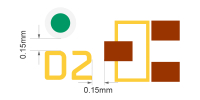
| Pad to silkscreen | >6mil (6mil≈0.15mm) | A minimum gap of 6mil is required to avoid silkscreen contamination on pads. This clearance helps prevent solderability issues, especially with HASL/ENIG finishes. |
|
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
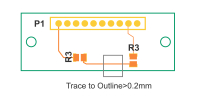
| Trace to outline | ≥0.2mm | For individually routed boards, copper traces must maintain a minimum clearance of 0.2mm from the CNC milled board edge. This ensures traces are not damaged during mechanical profiling. Reflects essential pcb manufacturing tolerances in precision routing. |
|
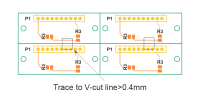
| Trace to V-cut line | ≥0.4mm | In panelized PCBs using V-scoring, traces must be kept at least 0.4mm away from the V-cut to avoid being compromised during separation. Critical for high-density designs using pcb panelization and automated depaneling. |
|
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panelization without space | 0mm | Zero spacing between boards in the panel. Commonly used in V-cut arrays where routing isolation is not required. Ideal for cost-effective pcb prototype fabrication service. |
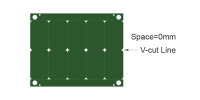
|
| Panelization with space | ≥1.6mm | When using routing (milling) for panelization, a minimum 1.6mm gap between PCBs is recommended for mechanical tool clearance and yield control. |
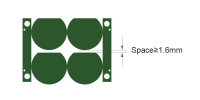
|
| Panelized round board | ≥80mmx80mm | Suitable for round PCBs with stamp holes (0.5mm diameter, 0.35mm copper gap). Default config includes 5–7 holes per break tab for stable panel strength. |
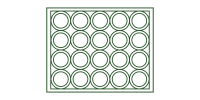
|
| Panelized castellated holes board | Panelize with stamp holes and add tooling strips on four board edges |
The distance between castellated hole and board corner should be > 4mm Recommended diameter of stamp hole is 0.5mm-0.8mm Recommended distance between the two stamp holes is 0.2mm-0.3mm |
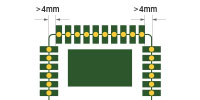
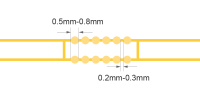
|
| Min. width of breakaway tab |
≥4mm
(≥ 5mm for mouse-bites) |
Breakaway tabs < 4mm can crack or tear during separation. For mouse-bite tabs, maintain ≥ 5mm width to reduce risk of corner lift-off or stress failure. |
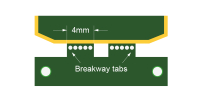
|
| Min. edge rails | ≥3mm | Edge rails provide mechanical support for SMT conveyors and reflow fixtures. Default panel includes 3mm edge rails on both long sides unless otherwise requested. |
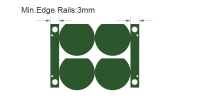
|
| Items | Manufacturing Capabilities | Notes | Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| PADS | copper-pour pattern | Default copper-pour uses hatch fill. If using solid pour, please confirm with NextPCB when placing an order to avoid copper connection errors. |
|
| 2D line | 2D elements in signal layers are not processable. Avoid placing 2D graphics in manufacturing layers, as they cannot be converted to copper features. | / | |
| Altium Designer Protel | Version | Different software versions may result in inconsistent Gerber generation. Please indicate your exact software version when submitting files. | / |
| Parts outside PCB | Ensure all components are within the PCB outline boundary. External placement will result in DRC failure and rejected files. | / | |
| solder mask opening | Do not confuse the paste layer with solder mask opening. NextPCB does not process paste layer Gerbers; any unintended openings will be ignored. |

|
|
| copper-pour pattern | Avoid using overly complex or excessively large fill areas. Recommended: use Polygon pour instead of solid fill to prevent region-loss errors during Gerber conversion. | / |
Precise cutting of base material to design dimensions
High-precision CNC drilling equipment
Photoresist coating and exposure development
Electroless and electrolytic copper plating
Removing excess copper to form circuits
Screen printing of solder mask ink
Printing component labels and text
Electrical testing and visual quality inspection
Printed Circuit Board Acceptance Standard
Quality Management System Certification
Environmental Compliance Certification
Safety Standard Certification
Professional engineers available to answer technical questions
+86 755 8364 3663
Detailed technical consultation and documentation support
support@nextpcb.comWeChat customer service and online chat support
Upload your design files for instant quote and professional advice