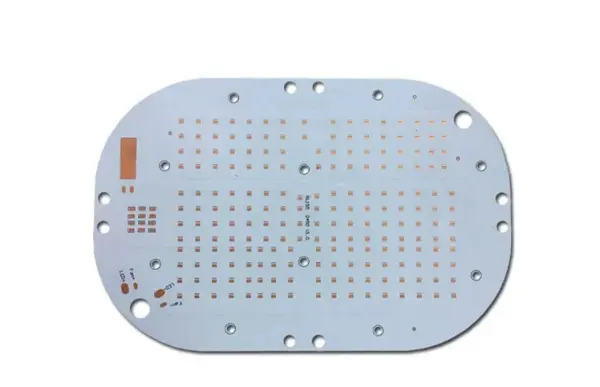
PCBs with aluminum metal core for efficient heat dissipation in high‑power designs.
- - Excellent thermal management and durability
- - Lightweight and cost‑effective
- - Good choice for LED/power electronics
- - Metallic core also helps EMI control
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
High-Tg PCBs are a go-to choice for advanced and mission-critical electronics where standard FR-4 may face a higher risk of warpage or delamination under lead-free reflow and repeated thermal cycling, higher layer counts, or tighter HDI densities. In this guide, we’ll explain what “High-Tg” really means, how to choose the right Tg range for your application, and why metrics like Z-axis CTE and Td matter for long-term reliability. If your project also involves high-speed or RF performance requirements, you can explore our Advanced PCB capabilities or compare materials in High-Frequency PCBs and Ceramic PCBs.
High-Tg or high glass transition temperature PCBs are printed circuit boards that utilize specialized substrate materials designed to withstand elevated operating temperatures. For this reason, High-Tg PCBs are sometimes referred to as high-temperature FR-4 PCBs, while truly high-temperature applications may require polyimide or other specialty laminates. NextPCB offers a variety of premium, industry certified High-Tg PCB material options for a multitude of industries and applications, ensuring performance, durability and reliability in the most demanding environments.
Tg stands for Glass Transition temperature, which is the temperature at which the substrate begins to soften and deform, compromising its mechanical and electrical properties. When the material is exposed to temperatures above its Tg rating for extended periods of time, the board is likely to bend and warp, or even delaminate.
FR-4 epoxy laminates are typically given a Tg rating or value, for example Tg130, where the number is the glass transition temperature in degrees Celsius. Typical Tg values include Tg130, Tg150, Tg170 all the way up to Tg250 and above. Certain industries and PCB designs require higher Tg values to ensure thermal stability in harsh environments and operating conditions. The typical Tg value for prototypes and consumer electronics is Tg130, and for other industries, please refer to the table below.
| Application | Tg Value (°C) | Tg Type | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics / prototypes | 130-150 | Low Tg/Mid Tg | Standard FR4 |
| Automotive, Industrial, High power LEDs, high-density designs | 170-180 | High-Tg | Enhanced FR4 |
| Aerospace, defense, high-power electronics | 180-220 | High-Temperature | Polyimide-based |
| High-Frequency, RF circuits, IC substrates, flex circuits | 220-250 | High-Temperature | PTFE (Teflon), Ceramic |
| 5G/mmWave, RF/microwave, Space electronics | >280 | High-Temperature | Rogers laminates |
If your primary driver is RF loss (Dk/Df) rather than temperature, see High-Frequency PCBs and Ceramic PCBs.
It is important to note that the glass transition temperature is not the absolute thermal limit to which a PCB board can be exposed to. Typical soldering temperatures can easily reach several hundreds of degrees, typically around 240–260°C, and even low-temperature solders have a melting point of around 140°C. Standard FR4 materials can be exposed to high temperatures for short periods of time without significant long-term impact.
For long-term reliability, the Tg value should always exceed the device’s maximum operating temperature. For instance, if a PCB's maximum operating temperature is 150°C, the substrate should have a Tg of 170°C or higher to prevent thermal degradation over time. As a good rule of thumb, the Tg rating of the substrate should be 20-25°C higher than the maximum operating temperature.
High-Tg substrate materials are chemically enhanced or engineered with specialized formulations to increase their glass transition temperature (Tg), improving their ability to withstand elevated temperatures. However, Tg value is just one factor when selecting substrate materials for high-temperature or thermally resistant PCBs. Other properties include:
These properties allow thermal stability for prolonged high-temperature operation, such as in aerospace, automotive, or power electronics applications.
Tg alone is not a full “heat rating”. For lead-free reflow and long-term reliability, engineers often evaluate additional thermal reliability metrics:
For advanced/high-reliability builds (multi-layer, HDI, repeated reflow), request Td, Z-CTE, and T260/T288 values alongside Tg when selecting materials.
NextPCB's standard quickturn and advanced PCB manufacturing services provide a wide range of PCB substrates to choose from. For the Standard PCB service, NextPCB offers KB and Shengyi low (Tg130), mid (Tg150) and high (Tg170) Tg laminates suitable for prototyping, semi-complex PCBs and consumer electronics. For PCBs with higher layer counts and HDI PCBs, we recommend choosing laminates with higher Tg ratings.
We also stock various laminates from internationally recognized suppliers, including Shengyi, TUC, ITEQ, Ventec, Arlon which are available via our Advanced PCB service. For PTFE laminates and ultra-high temperature requirements, please see our High Frequency PCBs and Ceramic PCBs.
| Material Code | Brand | Type | DK | DF | Tg/℃ | Halogen-free | Other | Data Sheet | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1000-2 | Shengyi | High Tg | 4.6 | 0.018 | 180 | Yes | Lead-free Process | S1000-2.pdf | Auto/industrial, power & LED, multilayer/HDI (lead-free, thermal cycling) |
| TU-768 | TUC | High Tg | 4.4 | 0.019 | 180 | Yes | Lead-free Process | TU768.pdf | Auto/industrial, power supply/module, high-layer boards (lead-free, reliability) |
| IT-180A | ITEQ | High Tg | 4.4 | 0.015 | 175 | Yes | Lead-free Process | IT180A.pdf | High-reliability multilayer/HDI, auto/industrial, power (lead-free, thermal cycling) |
| Material Code | Brand | Type | DK | DF | Tg/℃ | Halogen-free | Other | Data Sheet | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VT-901 | Ventec | Polyimide | 4.05 | 0.012 | 250 | Yes | Lead-free Process | VT901.pdf | High-temp & high-reliability, aerospace/defense, power electronics (polyimide, lead-free) |
| 85N | Arlon | Polyimide | 4 | 0.01 | 250 | No | Lead-free Process | 85N.pdf | High-temp, RF/microwave & harsh environments, aerospace (polyimide, lead-free) |
NextPCB can also support other types and laminate models, just enter the model number on the order form or contact us for details.

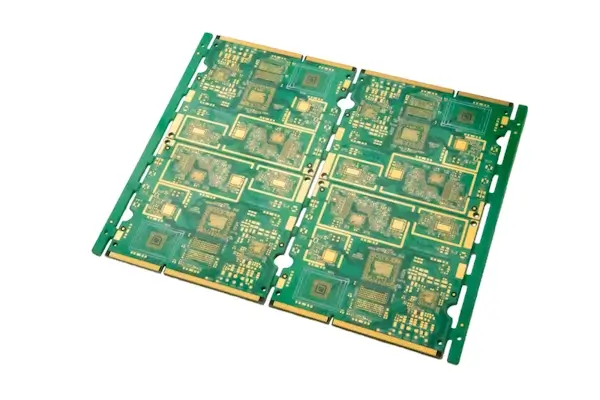

| Tg Rating | Tg170 |
| Laminate Manufacturer | Kingbrother (KB) |
| Substrate Type | FR4 |
| Layer Count | 8-layer HDI I |
| Board Thickness | 1.0mm |
| Dimensions | 140 x 140mm |
| Surface Finish | ENIG + Gold Fingers |
| Solder Mask Color | Green |
| TG Rating | TG170 |
| Laminate Manufacturer | Shengyi (SY) |
| Substrate Type | FR4 |
| Layer Count | 12-layer HDI II |
| Board Thickness | 2.5mm |
| Dimensions | 50 x 36mm |
| Surface Finish | ENIG |
| Solder Mask Color | Green |
| TG Rating | TG170 |
| Laminate Manufacturer | Shengyi (SY) |
| Substrate Type | FR4 |
| Layer Count | 12-layer HDI II |
| Board Thickness | 2.5mm |
| Dimensions | 50 x 36mm |
| Surface Finish | ENIG + Gold Fingers |
| Solder Mask Color | Green |


Entrust your mission-critical products to NextPCB's safe hands. With over 15 years of experience delivering exceptional PCBs for the most demanding applications, NextPCB ensures reliability, precision, and high-performance circuit boards from prototype to deployment.
In most PCB material classifications, High-Tg FR-4 typically refers to Tg ≥ 170°C. Compared with standard FR-4 (often around 130–150°C), High-Tg laminates offer better thermal stability and mechanical strength under lead-free reflow and repeated thermal cycling.
No. Tg is not the absolute thermal limit. It indicates when the resin system transitions and begins to soften, which can increase warpage and delamination risk over time. For heat reliability, engineers also check Td, Z-axis CTE, and T260/T288 (time-to-delamination)—especially for advanced builds.
High-Tg is recommended when your board will see lead-free reflow, multiple reflow cycles or rework, high layer counts, or harsh thermal cycling (common in automotive, industrial, and power electronics). As a practical guideline, aim for a laminate Tg that is about 20–25°C higher than the maximum operating temperature.
High-Tg focuses on thermal stability and reliability, while High-Frequency materials focus on RF loss performance (low Dk/Df and stable electrical properties). If your primary driver is signal loss, impedance control, or GHz-range RF/microwave performance, you should compare High-Frequency PCBs (and in extreme thermal cases, Ceramic PCBs) rather than selecting by Tg alone.
Often, yes. Multilayer and HDI boards are more sensitive to Z-axis expansion and thermal stress during lamination and assembly. Choosing a High-Tg (or higher-reliability) laminate can reduce warpage and improve plated-through-hole integrity across thermal cycling, especially when combined with appropriate Td/Z-CTE/T260/T288 targets.
PCB is the abbreviation of the...