
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comFor startups, engineers, and innovators, small batch PCB production bridges the gap between prototyping and mass manufacturing. Unlike mass production, which requires thousands of units, small batch PCB manufacturing allows you to produce 50-500 units cost-effectively while maintaining design flexibility. This guide covers everything you need to know about small batch PCB production, from its benefits to best practices for ordering.

Small batch PCB production refers to manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards in quantities typically ranging from 50 to 1000 units. However, definitions may vary across manufacturers, with some utilizing total production area as the primary classification metric. It serves as a critical phase between prototyping (1-10 units) and mass production (thousands+ units). This stage is ideal for:
Compared to pcb prototyping, small batch pcb production offers better cost per unit due to optimized workflows. Compared to mass pcb production, it retains flexibility for design tweaks without significant tooling costs.
| Stage | Objective | Typical Quantity | Key Characteristics |
| Prototyping (Quick-turn) | Design Verification | 1–10 units | High flexibility, rapid iteration, and higher per-unit cost. Focuses on "Proof of Concept." |
| Small-Batch (Small Run, Low volume) | Design Validation & Trial Production | 50–1,000 units | Balances flexibility and efficiency. Used for functional testing, certifications (UL/CE), and initial market entry. |
| Mass Production | Large-scale Stable Supply | 1,000+ units | High efficiency, lowest per-unit cost, and optimized for high yield and process stability. |
Lower per-unit costs: While pcb prototyping costs are slightly higher due to setup expenses, small batch production spreads these costs over more units, reducing the per-unit price significantly.
Example: A prototype batch of 10 units might cost $13 total ($1.3/unit), whereas a small batch of 200 units could cost $209.27 ($1.05/unit)—a 19.23% cost reduction per unit.
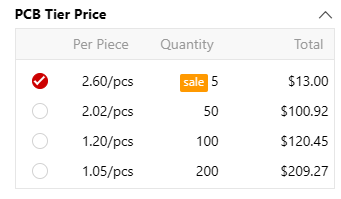
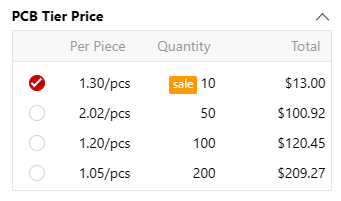
4 layer pcb, fr-4, 100*100mm
Easier modifications: Unlike mass production where design changes are costly, small batch allows engineers to refine PCBs based on testing feedback.
Ideal for startups: Startups can iterate designs without committing to large volumes, minimizing financial risk.
Reduced lead times: Small batch production avoids the lengthy setup of mass production lines, enabling quicker delivery for market testing or initial sales.
Competitive edge: Helps businesses launch products faster than competitors relying on traditional mass production cycles.
Comprehensive testing: Allows thorough functional testing and quality checks before scaling up.
Risk mitigation: Identifies issues early, preventing costly recalls or redesigns in mass production.
Tailored solutions: Perfect for specialized industries like medical devices or aerospace, where custom PCBs are needed in limited quantities.
Low-volume demand: Meets needs for products with uncertain market demand, avoiding overproduction.
PCB design: Engineers create detailed schematics using tools like Altium Designer or Eagle.
DFM checks: Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reviews ensure the design is feasible for production, catching potential issues early.
PCB materials: Choose substrates (e.g., FR-4), copper weights, and surface finishes based on application needs.
Component sourcing: Select resistors, capacitors, and ICs from suppliers like Digi-Key or Mouser, ensuring quality and availability.
Steps: Includes panelization, drilling, plating, etching, solder mask application, and silkscreen printing. Learn the complete PCB fabrication process
Quality control: Automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray checks verify accuracy and detect defects.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology): Components are placed using pick-and-place machines, then soldered via reflow ovens.
Through-hole assembly: For components requiring stronger connections, manual or automated insertion and wave soldering are used.
Testing: Functional tests (e.g., ICT, flying probe) ensure PCB performance before shipping.
In-circuit testing (ICT): Checks electrical connectivity and component values.
Functional testing: Simulates real-world conditions to validate PCB behavior.
Burn-in testing: Stress tests PCBs under operating conditions to identify early failures.
Experience: Select a manufacturer with expertise in small batch production, ensuring quality and reliability.
Capabilities: Verify they offer the services you need, such as SMT assembly or through-hole mounting.
Reviews: Check customer feedback and case studies to assess reliability and service quality.
DFM guidelines: Follow manufacturer recommendations for trace widths, spacing, and drill sizes to avoid production issues.
Design tools: Use software like Altium Designer or KiCad for accurate and manufacturable designs.
Lead times: Account for component availability delays to avoid production bottlenecks.
Quality: Ensure components meet specifications and are sourced from reputable suppliers.
In-house testing: If budget allows, invest in testing equipment for thorough quality checks.
Manufacturer testing: Utilize the manufacturer's testing services for comprehensive assurance.
→Learn NextPCB's Quality control process
Documentation: Maintain detailed design and production records for future scaling.
Supplier relationships: Build strong ties with manufacturers and suppliers to streamline scaling processes.
Solution: Optimize designs for manufacturability and work with manufacturers to reduce costs.
Solution: Plan ahead, maintain buffer inventory, and choose suppliers with reliable lead times.
Solution: Implement rigorous testing protocols and collaborate with experienced manufacturers.
Solution: Conduct thorough DFM reviews and prototype testing before small batch production.
Small batch PCB production is a vital phase for startups, engineers, and innovators. It offers cost-effective, flexible, and efficient PCB manufacturing, enabling design validation, market testing, and low-volume applications. By following best practices—choosing the right manufacturer, optimizing designs, and planning for scaling—you can leverage small batch production to bring your PCB projects to life successfully.
Whether you're developing a new product or need custom PCBs for niche applications, small batch PCB production provides the balance between prototyping and mass production that your project demands.
All Files Ready? Get Your Price Online
>> Recommend reading: PCB Mass Production Guide: Key Steps from Prototyping to Scaling Up
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now