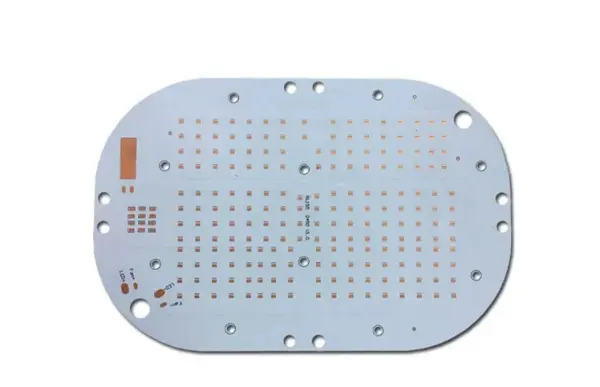
PCBs with aluminum metal core for efficient heat dissipation in high‑power designs.
- - Excellent thermal management and durability
- - Lightweight and cost‑effective
- - Good choice for LED/power electronics
- - Metallic core also helps EMI control
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
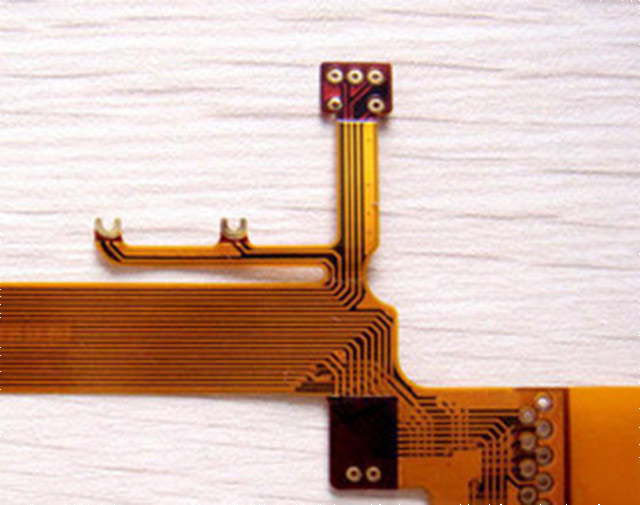
Flexible PCBs (FPCs), also known as flex PCBs or flexible circuit boards, are printed circuit boards made of bendable substrate materials such as polyimide (PI), allowing them to twist, fold and conform to tight spaces or precise shapes. Flexible printed circuit boards remain indispensible in applications where the space is limited or non-planar, or where dynamic movement is required.
The unique properties and advantages of flex PCBs make them suitable for a wide range of applications which would be impossible or vastly inferior with conventional rigid alternatives.
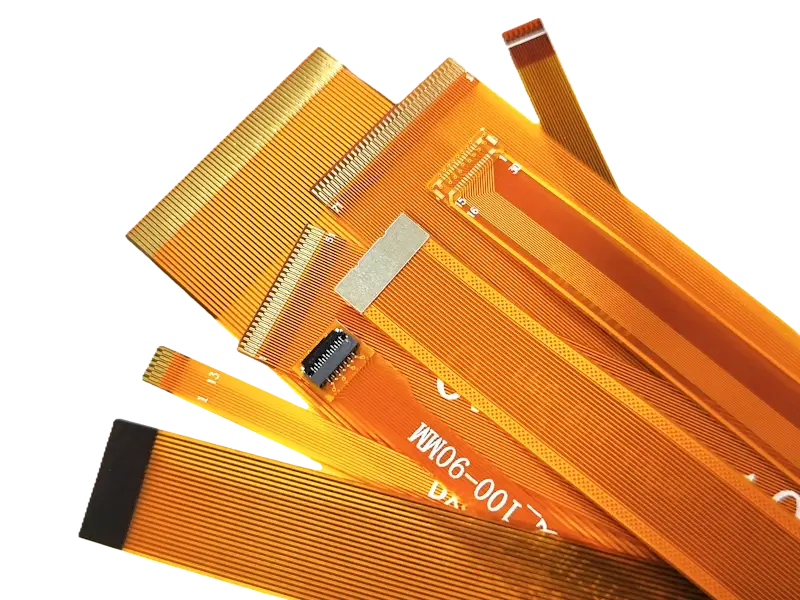

Custom flex cable PCBs with various stiffeners and connectors
NextPCB provides PCB manufacture and assembly of various flex PCB types from simple flex cables to the most demanding applications including:
Flex PCBs are printed circuit boards constructed entirely of flexible materials. The most common type is made of polyimide (PI) where copper traces and pads are laminated onto a thin sheet of PI, which are then covered with another sheet of PI film called the coverlay. Adhesives hold all the layers together to make a thin printed circuit board that can withstand thousands of bend cycles while maintaining mechanical and electrical performance.

Most FPCs are yellow due to the natural color of polyimide base material. Though they can be dyed different colors.
Flex PCBs come in many different forms and can be manufactured using a variety of different materials and techniques to suit different applications. Here are some of the most common:
Polyimide Flex PCBs: PI, also known by the branded name, Kapton®, polyimide is a strong temperature resistant polymer found everywhere from solar panels to satellite thermal insulation. It makes a great material for flex PCBs thanks to it's exceptional thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties and can easily integrate multiple conductive layers while maintaining a thin profile.
LED Flex PCBs: LED flex PCBs for lighting applications include LED strips, LED lightbulbs and torches. Polyimide is commonly used for the base substrate but the surface is covered in a flexible white or black solder mask to offer better reflective or absorption properties. Thick aluminum foil backing and heavy copper are options to improve heat transfer and reinforce the PCBs.
Thin FR4 Flex PCBs: Circuit boards with a degree of flexibility can be achieved using thin FR4 substrates. While regular FR4 boards have a final thickness of 0.8 to 2.5mm, thicknesses as low as 0.4mm to 0.1mm are possible with thinner cores which give the boards a degree of flex. Though less common than PI PCBs, these PCBs are suitable for static installations where the PCBs are bent and held in place permanently, or low-flex applications that require minor bending while retaining the advantages of rigid PCBs.
Semi-flex PCBs: Semi-flex PCBs are also made of standard FR4 materials but have the thickness partially milled to create a bend area, effectively achieving a rigid-flex structure. This z-axis milling technique can also be used to create bend areas in metal core PCBs such as aluminum core circuit boards. Such boards are not suited for repeated bending however.
Rigid-Flex PCBs: Rigid-flex circuit boards consist of both rigid and flex areas, typically by sandwiching layers of polyimide between FR4 substrates. The flex sections are reserved for bending and signal transfer while the rigid sections house the components and intricate circuitry, achieving the best of both worlds. Though much more expensive than pure flex PCBs, rigid-flex PCBs
Flex PCBs offer three primary advantages over their rigid counterparts that make them invaluable in a wide range of products and applications. Their lightweight design, ultra-thin profile and the ability to bend or conform to various configurations mean they can be found in everything from earpods, touch interfaces, foldable electronics, medical devices, mechatronics, light strips, and anything that has an LED or LCD display.
While flex PCBs offer a unique set of advantages, their inherent flexibility introduces complexities across the entire product lifecycle, from design to manufacture to assembly and deployment. Engineers should be well aware of the limitations and constraints before beginning a flex PCB design for optimal manufacturability and reliability.
Restricted component placement: Component placement is limited to non-bend areas, areas with low bend frequency or low bend radius. FPCs are flexible, but solder joints are not. Excessive bending can cause joints to crack or tear from the substrate. Stiffeners can be used for reinforcement, however, this takes up space on one side and essentially limits component placement to a single side.
Low component density: Manufacturing limits and tolerances for flexible PCBs are not as refined compared to rigid based alternatives. Alongside the additional bend and mechanical considerations, this impacts how close components and traces can be placed together.
Copper and layer count limitations: The number, thickness and layout of copper layers can have a significant impact on the bend radius and bend frequency. As such, this limits the complexity and current carrying capacity of flex circuits. Design techniques such as using hatched over filled copper pour, removing coverlay in bend areas and using lower copper thicknesses can be used to increase flexiblility in bend areas.
Design challenges: The dynamic and fragile nature of flex PCBs mean extra care and additional design techniques are required to maintain the structural integrity of a flex PCB during it’s lifetime. For more design techniques with examples, take a look at our flex PCB design guide on Wevolver.
Difficulty of manufacture and PCB assembly: While polyimide has excellent heat resistant properties (typically 250-280°C), without careful consideration and process control, flex PCBs are prone to shrinking and delamination during the soldering process. The design of solder fixtures must take this into account and limit exposure to heat to only where necessary. Even for small batch and prototype runs, a fixture is recommended to facilitate component placement and soldering, adding to production costs.
At NextPCB, we specialize in a wide variety of flex PCBs, offering a broad selection of options and features for any application.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Flex Circuit Layers | 1 to 6 layers |
| PI Base Material |
|
| Covering Type | PI Coverlay or Flexible Solder mask |
| Surface Finishes | ENIG, OSP and electroplated gold |
| ENIG Gold Thickness | 1 to 3μ" |
| Flex PCB Thickness | 0.1 to 0.45mm |
| Copper Thickness | 1/3 to 2 oz |
| Min. Trace width/spacing | 2/2 mil |
| Min. Drill Hole Diameter | 0.1mm |
| PCB Solder Mask Color |
|
| PCB Stiffener Options | FR4, PI, aluminum and stainless steel |
| Extras |
|
Please inquire for advanced capabilities.
PCB is the abbreviation of the...