Stacy Lu

Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comVarious PCB types are based on their configurations, and they have a broad range of applications in the electronics domain. This article explains the single-layer flex PCB including its design considerations.
In this article,
Single Layer Flex PCB is one of the most popular flex PCB circuits. It has a single conductor layer that consists of the conductive polymer of the dielectric films. Based on the design requirement, the etched copper layer produce the specific circuit pattern. The polyamide coverlay helps in insulating and protecting the environment of the circuit. It supports the inclusion of pins, electronic components, and connectors. Its flexible Substrate allows them to bend, conform and twist to different shapes and sizes, making them ideal for broad applications.
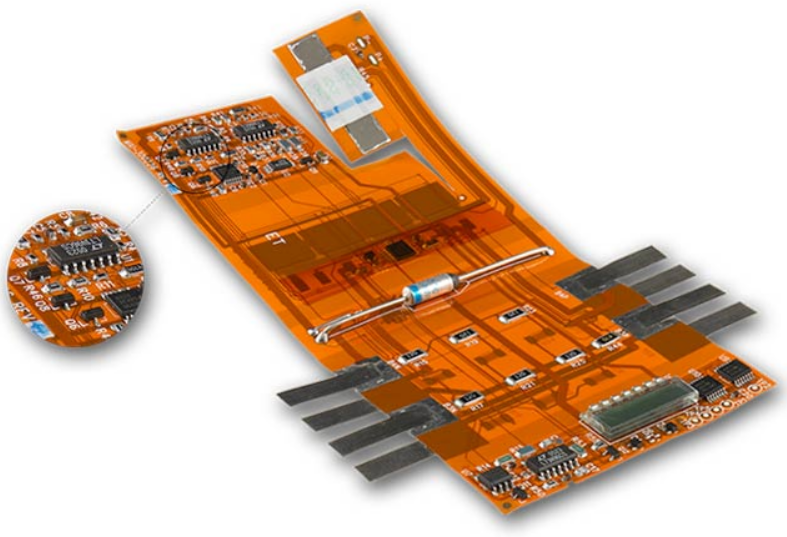
Single Layer Flex PCB is a versatile and high-performing technology that provides various advantages compared to rigid PCBs.
Single Layer Flex PCB is one of the most popular flex PCB types. It offers a wide range of advantages in the commercial market today. Some of its benefits include the following:
Flexibility - Flex PCB's flexibility helps provide the third dimension that allows working with as they interconnect two or more planes during execution. Thus, it solves the space and weight problems compare to that rigid PCBs. Besides, it can be manipulated or modified several times during execution and installation without electronic failure.
Reduce Assembly Times and Cost - Flex PCB requires less workforce during assembly and thus helps to reduce production errors. Besides, it eliminates the high cost of routing, soldering wires, and wrapping. Instead of individual rigid PCB boards, the complete interconnection system is installed and replaced. It helps to reduce errors and helps to reduce manufacturing costs as well.
Freedom in Design- Flex circuits offers design flexibility that rigid boards cannot match due to their ability to bend and conform to three-dimensional shapes. With the flexibility of wires or ribbon cables, the possibilities for flex circuit design are virtually limitless. At NextPCB, we take pride in tackling even the most complex design challenges. Flex circuits can be customized to meet incredibly complex and innovative configurations while functioning reliably in harsh environments.
Increase Heat Dissipation - Flex PCB has a larger surface-to-volume ratio. Also, it has a compact design nature. Thus because of this nature, it allows a shorter thermal path. Furthermore, the thinner design of the flex circuit helps in proper heat dissipation from both sides of the circuit.
Besides, the single-layer flex pcb offers other benefits like point-to-point wire replacements, reliability, durability, improved airflow, increased system reliability, etc. Thus, compared to single-layer rigid PCB, it has a wide range of popularity.
| Type | IPC 6013 |
|---|---|
| Description |
|
| Configurations |
|
| Flex Core Materials |
|
| Coverlays |
|
| EMI/RF Shielding |
|
| Pressure Sensitive Adhesives |
|
The single-layer flex PCB has mainly two structural application-Static and Dynamic Applications. In static applications, flexible circuits can utilize flex-to-fit or flex-to-install applications, where the circuit is only flexed during installation to fit it into the intended application. In such static applications, Electro Deposited (ED) copper, which is less expensive, is typically used.
Whereas in dynamic applications, the flexible circuit is dynamically flexed during the actual use of the final product. Common examples of this application include laptops, printer heads, arms, cell phones, etc.
Some of the common applications include:
The common materials used in single-layer flex PCB include
Conductors- Copper is one of the most widely used conductors in this PCB. It has various thicknesses that meet the requirement of each customer. Furthermore, the conductor option includes the following:
Adhesives- The selection of adhesive depends on customers' needs and requirements and the conductor's thickness. Some of the standard adhesives include
Insulators- Flexible Substrate, also called base substrate, and the coverlay materials are available in a wide range of thicknesses from several manufacturers. Some of the common insulators include
Finishes- The final finish depends on the requirement of customers and the application of the finished product. Some of the common finishes include
Single-layer Flex PCB design requires a different approach compared to rigid PCBs. The well-designed flex PCB is lightweight, durable, reliable, and easy to install. Thus, it has wide applications in wearable devices, IoT devices, satellites, etc.
In flex board design, you need to consider various factors like the outline of the board, bending requirements, stack-up, material selection, the position of copper features, and cost factors. Some of the primary factors use for designing the flex PCB are as follows:
Flex PCB's flexible nature helps the designer use them in any tiny package. The important things to understand about this flex PBC are the board flexing times and to what extent it will flex. The dynamic board should be robust and needs to withstand the tens of thousands of bends during its operation. In contrast, the static board flexes less than 100 times during operation. Thus, the bend times determine whether the PCB is dynamic or static. Therefore, it is one of the vital factors to consider while designing your single-layer flex PCB.
Before selecting your single-layer flex PCB, you should know the PCB materials, including the characteristics that suit the design criteria. The properties of materials include; moisture absorption, fire retarding, dielectric constant, and coefficient of thermal expansion.
While designing the flex board, knowing the risk of using the vias is vital. In the case of flex PCBs, the vias can easily break or crack the peel. The teardrop-shaped vias can mitigate this error. Also, try to keep the angular rings large as possible.
Flex circuits can incorporate specific areas that are optimized for surface mount components. The coverlays used in flex circuits are laser-cut, enabling intricate and irregularly shaped openings to be created for dense surface mount patterns. Additionally, photo-imageable coverlay materials offer even greater flexibility in designing layouts for surface mount components. This level of customization allows for greater design freedom and can result in more compact and efficient electronic systems.
Matching impedance refers to the correct function of the signal and circuit board. Thus, the factors like relative permittivity of materials, trace width, signal trace distances from plane layers, and trace thickness can affect the impedance of flex.
Besides, the operating environment, pad fillets, conductors, and routing and assembly considerations are some of the factors that need to consider this factor while designing the flex PCB.
The manufacturing process of single-layer flex PCB includes the following factors:
Etching: It is one of the first processes in PCB manufacturing. In this process, the circuit pattern is etched into the board. The process creates the desired conductive and insulating patterns using etching, photolithography, and other techniques.
Substrate Preparation: It should prepare the flexible Substrate that ensures the proper adhesion of the circuits. It involves cleaning the Substrate and finally applying the thin layer of adhesive.
Assembly: The components are assembled into the circuits using surface mount technology or other assembly techniques.
Testing: Finally, the single-layer flex PCB requires testing to ensure proper performance and functionality. This includes electrical testing, environmental testing, and reliability testing.
Single-layer flex PCBs are a versatile and high-performing technology. Further, it offers several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs. They have wide applications, from wearable and consumer electronics to industrial and medical equipment.
NextPCB provides all PCB-related services. We can help you through all your PCB designs, including Single layer, multi-layer, right, and flex. You can request a quote to learn more about our services. Feel free to contact us.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now