Introduction to Ultrasonic Welding
Using high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations, ultrasonic welding joins two materials together in a solid form. Mechanical vibrations at high frequencies (usually between 15 kHz and 70 kHz) are applied to the materials to be connected.
This technique involves applying pressure to a connection while using an ultrasonic instrument or horn to fuse the materials together. Materials are melted and fused together because their molecules vibrate and brush against one another in response to the horn's vibrations.
This technique can join metals, ceramics, glass, and thermoplastics.
Because of its speed, consistency, and reliability, this joining process is used in the automotive, medical, packaging, and electronics industries.
How Does Ultrasonic Welding Work?
This technique works by applying high-frequency mechanical vibrations to the materials being joined. These vibrations create friction and heat that melts and fuses the materials together. Here is a detailed explanation of how the process works:
- Preparation: The materials to be joined are first cleaned and prepared by removing any surface contaminants or oxidation. The materials are then placed in the welding fixture and aligned.
- Clamping: The materials are clamped together using a fixture that holds them in position. Then applies a specific amount of pressure. The pressure applied should be sufficient to keep the materials in place during the welding process.
- Ultrasonic horn: The ultrasonic horn, is a vibrating tool made of a metal alloy such as titanium. The horn is connected to an ultrasonic generator that produces high-frequency electrical energy.
- Vibrations: The ultrasonic generator converts the electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical vibrations, typically between 15 kHz and 70 kHz. These vibrations are transmitted to the horn and then to the materials being joined.
- Heat generation: The mechanical vibrations cause the molecules in the materials to rub against each other, creating friction and heat. The heat generated softens the materials and causes them to melt at the contact point.
- Weld testing: The welded junction is next evaluated for strength and quality. This is to make sure it complies with the necessary requirements.
Ultrasonic welding is a quick and effective method of connecting materials because the entire procedure takes only a few seconds.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding has several advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of them:
Advantages:
- Quickness: Ultrasonic welding is a quick procedure that can quickly combine materials, making it perfect for high-speed production settings.
- Precision: The procedure may create welds of excellent quality and consistency thanks to its high level of precision.
- Energy efficiency: Compared to other welding techniques like hot plate welding or vibration welding, ultrasonic welding is a procedure that consumes less energy.
- Non-invasiveness and versatility: With no need for additional materials or adhesives, the process is non-invasive and does not affect the materials being joined. Additionally, ultrasonic welding can be used to join a wide range of materials, from ceramics and metals to polymers.
Disadvantages:
- Material limitations: While this can be used to join a wide range of materials. Some materials are not suitable for the process due to their high melting points or other properties.
- Equipment cost: Ultrasonic welding equipment can be expensive to purchase and maintain. That may be a barrier to adoption for smaller manufacturers.
- Joint strength: The strength of the weld joint may not be as high as other welding methods. Examples, hot plate welding or vibration welding.
- Joint design limitations: The design of the joint may be limited by the requirements of the ultrasonic welding process, which may affect the overall design of the product being manufactured.
- Surface preparation: The materials being joined must be prepared and cleaned properly to ensure a strong and consistent weld, which can be time-consuming and add to the overall manufacturing cost.
Applications of Ultrasonic Welding in Various Industries
In the printed circuit board (PCB) business, this technique has numerous applications, such as:
- Wire Bonding: This technique can be used to bond wire leads to PCBs, producing a stable electrical connection between the wire and board. This method is frequently employed in the fabrication of semiconductor devices.
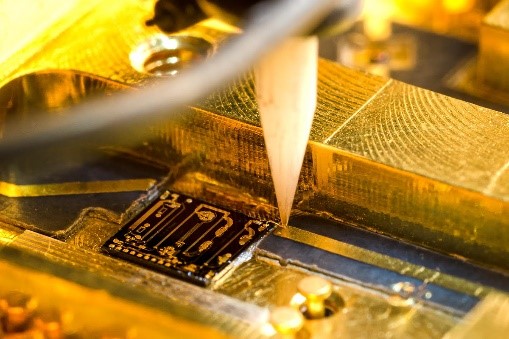
- Soldering: This technique can be used to solder components to printed circuit boards (PCBs), establishing a robust and dependable connection. This method is especially beneficial for surface-mount technology (SMT) components.
- Sealing: This technique can be used to establish a hermetic seal around components on a PCB, preventing the ingress of moisture and other impurities.

- Connector assembly: This technique can be used to assemble connectors onto a PCB, thereby establishing a secure electrical connection between the connector and the board.
- Packaging: This technique can be used to build a secure and tamper-evident container for PCBs, safeguarding them from damage during transport and storage.
Wire bonding and packaging are only two of the many uses for ultrasonic welding in the printed circuit board (PCB) industry. It's a great choice for mass manufacturing because it's fast, reliable, and produces uniform outcomes.
Materials Suitable for Ultrasonic Welding
This technique can be used to join a variety of materials, including:
- Plastics: This technique is commonly used to join thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and PVC.
- Metals: This technique can be used to join metals such as aluminum, copper, and nickel.
- Ceramics: This technique can also be used to join ceramics such as alumina and zirconia.
- Composites: This technique can be used to join composite materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers.
- Fabrics: This technique can be used to bond synthetic fabrics such as nylon and polyester.
In general, materials that can be melted and solidified quickly under the heat and pressure of ultrasonic welding are suitable for the process. The materials should also be compatible with the frequency and amplitude of the ultrasonic vibrations used for welding. The specific welding parameters used will depend on the material being joined and the requirements of the application.
Comparison of Ultrasonic Welding with Other Welding Techniques
This technique is a one-of-a-kind welding method that, like any other method, has its benefits and drawbacks. comparison of ultrasonic welding to other common welding methods below.

Ultrasonic and laser welding: Non-contact welding methods that generate a focused heat source include ultrasonic and laser welding. However, This technique is more suitable for plastics and other non-metallic materials, while laser welding is better suited for welding metals.
Ultrasonic welding and hot plate welding are two prominent methods for joining polymers together. This technique is a speedier procedure that doesn't need any preheating, while hot plate welding takes longer because the materials have to be heated up beforehand.
Third, the difference between ultrasonic welding and vibration welding is that both utilize mechanical vibrations to create heat and join materials. Yet, the higher frequencies and lower amplitudes generated by ultrasonic welding might lead to a more uniform and exact weld.
Ultrasonic welding and friction welding are two types of mechanical welding that employ similar principles to create heat and join materials. Ultrasonic welding, on the other hand, works better with plastics and other non-metallic materials than friction welding does.
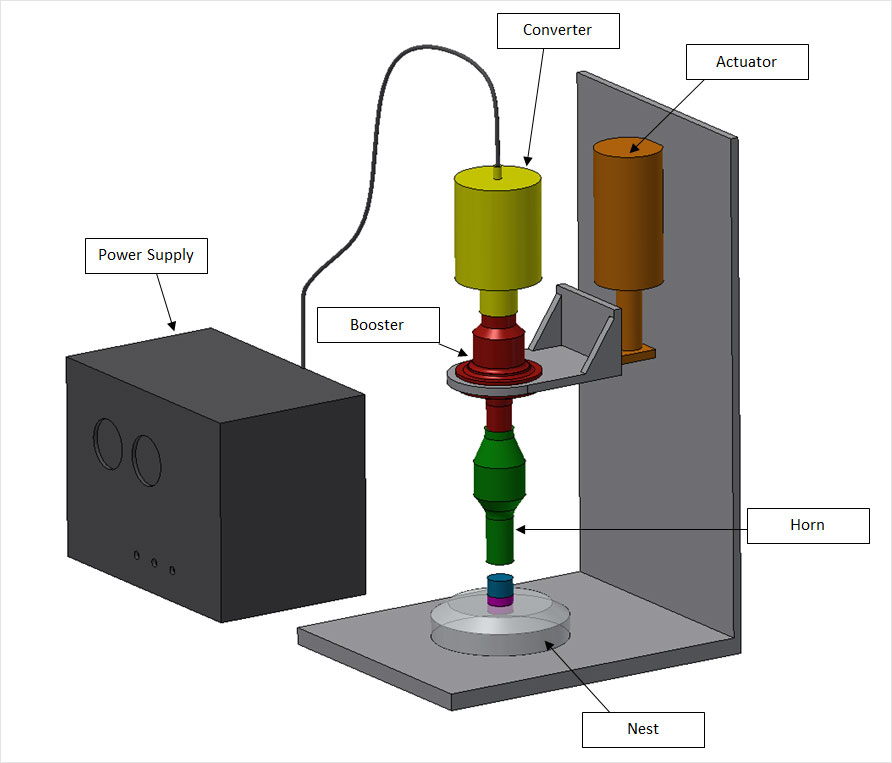
Ultrasonic Welding Equipment and Machinery
Equipment and machinery typically consist of the following components:
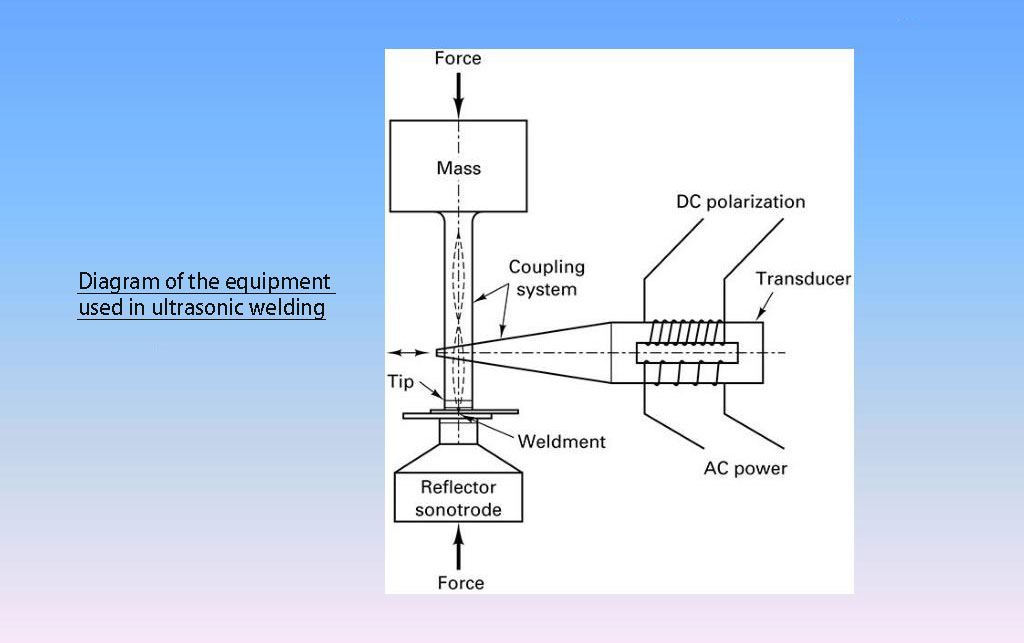
- Ultrasonic generator: This is the main component of this technique. It generates high-frequency electrical energy that is then converted into mechanical vibrations by the transducer.
- Transducer: The transducer converts high-frequency electrical energy into mechanical vibrations that are transmitted to the tooling.
- Horn: The horn amplifies and focuses the mechanical vibrations generated by the transducer onto the materials being welded.
- Anvil: The anvil is a flat surface that supports the materials being welded and applies pressure to the joint during welding.
- Control unit: The control unit monitors and adjusts the welding parameters, such as frequency, amplitude, and pressure, to ensure consistent and high-quality welds.
- Tooling: The tooling consists of a fixture or a nest that holds the materials being welded in place during the welding process.
This equipment can be customized to suit specific applications and materials. For example, the shape and size of the horn and anvil can be customized to accommodate different joint designs and materials. Additionally, some equipment may include additional features such as temperature sensors, force sensors, and servo motors for more precise control over the welding process.
Safety Precautions for Ultrasonic Welding
One of the most crucial precautions to take when using this equipment is to have proper training. Individualized instruction on the equipment's operation and the dangers and hazards it poses should be provided to operators. Such instruction has to focus on areas like:
- Setting up, adjusting, and troubleshooting ultrasonic welding equipment all require skilled operators who have received proper training
- Procedures for ensuring worker safety
- When working with this equipment, employees should be instructed in the right use of PPE, ventilation measures, and tool handling.
- Operators should know how to use the emergency stop button and respond to accidents.
- Operators must recognize wear and repair ultrasonic welding equipment.
- Businesses can train ultrasonic welding personnel to understand the dangers and use the equipment safely and effectively.
Noting that these safety precautions are not exhaustive, operators should always refer to the manufacturer's instructions and industry regulations for specific safety recommendations. In addition, operators must be aware of any special risks related with the materials being welded and take the necessary precautions to mitigate these dangers. By placing an emphasis on safety during ultrasonic welding processes, operators may maintain a productive and secure work environment.
Conclusion
Ultimately, ultrasonic welding's efficiency and adaptability make it a useful tool for a wide range of industries. Its advantages over conventional welding methods include shorter cycle times, better welding process control, and the ability to join dissimilar materials. However, ultrasonic welding has certain major downsides and restrictions, such as the need for pristine surfaces and the inability to combine specific materials. Training and precautions should be taken before employing ultrasonic welding equipment. In conclusion, ultrasonic welding is a valuable resource for a wide range of industrial uses and is likely to remain an important technological advancement for the foreseeable future.







