
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com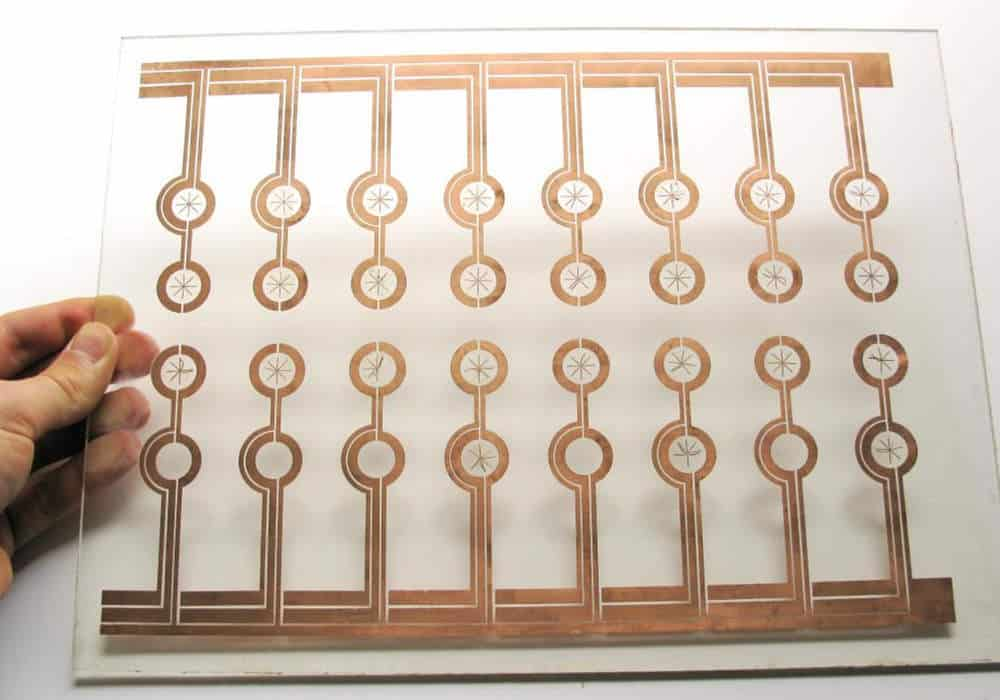
Transparent PCB means light can pass through it, and humans can discern its internals. Optics is very important in Technology, and the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) industry is witnessing tremendous changes in Printed Circuit Board designs thanks to Transparent glass technology.
Applying a transparent printed circuit board is noteworthy, especially in 5G networks. Experts believe that using transparent Printed Circuit Boards in 5G would significantly change our means of digital communication in unimagined ways.
This guide presents information regarding Transparent Printed Circuit Boards. It also highlights the materials needed to design and construct a transparent Printed Circuit Board, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and worldwide applications.
A transparent Printed Circuit Board (or PCB) is a see-through circuit board that lets you see its internal components. A transparent Printed Circuit Board contains fully transparent or semi-transparent conductive paths and components.
Its applications are often flexible depending on the material used in designing a transparent Printed Circuit Board. The materials usually consist of polyester, polyimide, and ceramic materials.
Its many applications include medical devices, mobile phones, cameras, automatic control systems, instrument panels, ABS systems, smart contact lenses, and electronic skins.
Transparent Printed Circuit Boards are rigid or flexible, depending on the material used in constructing such circuit boards. Flexible transparent circuit boards do not mean they are weak and easy to break; instead, they have specific resistance properties.
The flexible transparent Printed Circuit Boards base material is usually polyester and polyimide. These materials provide almost complete (about 95%) transparency in their transparent Printed Circuit Board designs. Each material has various conductive and thermal properties.
Flexible Transparent PCB made with polyimide are found to be resistant to thermal pressures. Also, they can withstand electrical and mechanical stress. Because of these high resistive properties of polyimide, electronic manufacturers can design transparent Printed Circuit Boards in any shape and size. Also, they make them in several colors like light blue, light green, white, transparent, light brown, and others.
For rigid transparent Printed Circuit Boards, for example, ceramic Printed Circuit Boards contain an aluminum substrate, which could be Aluminum oxide, Aluminum & Magnesium Amalgam, or Magnesium oxide. These kinds of transparent Printed Circuit Boards offer about 80% transparency.
Depending on the material employed in designing a transparent Printed Circuit Board, they offer high resistance to moisture and dust. Based on the materials, there are three kinds of Transparent Printed Circuit Boards in the Printed Circuit Board industry; Glass, Ceramic, and Transparent.
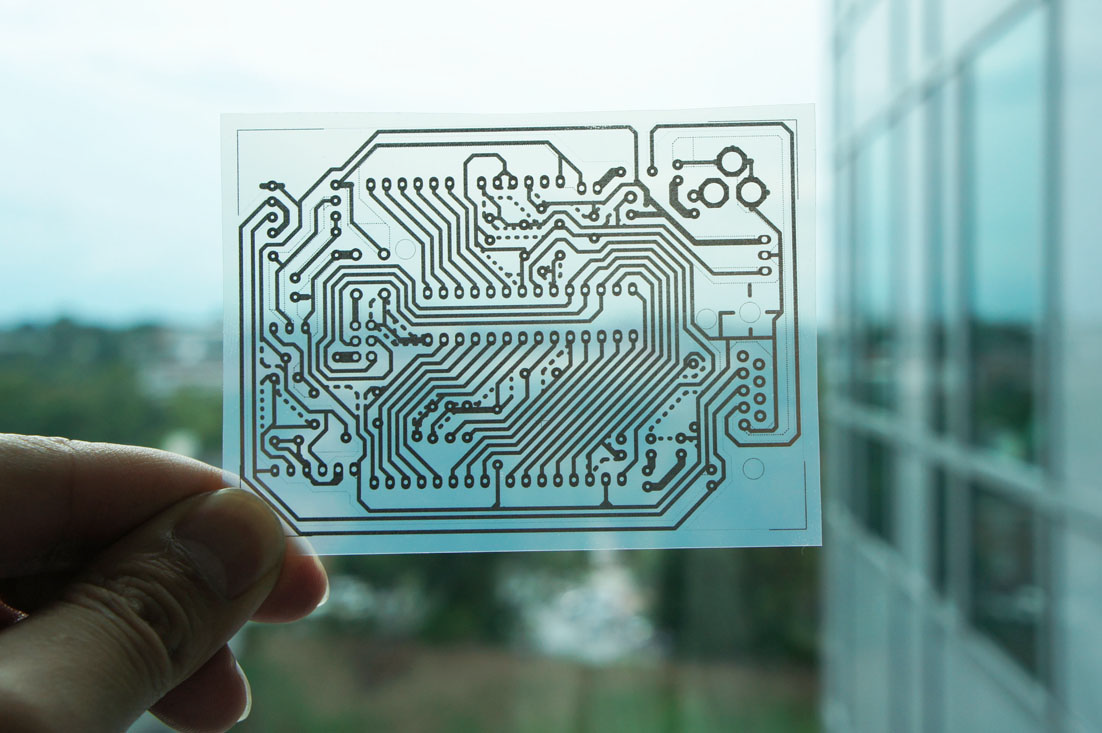
Glass is made using a mixture of limestone, soda, sand, and ash. These materials are inexpensive, easily recycled, and abundant in nature, making glass safe for the environment. Glass Transparent Printed Circuit Boards offer total luminescence, meaning light can pass through them in all directions.
However, to design a Glass Transparent Printed Circuit Board, regular glass cannot be used since it is not durable and easily breaks. Tempered glass is majorly used in the manufacture of glass Printed Circuit Boards. It is a reprocessed glass that maximizes durability. It offers improved shock and impact absorption capabilities than regular glass. Tempered Glass Transparent Printed Circuit Boards are excellent for extreme applications.
Sapphire Glass is another material used in the glass transparent circuit board design. It is the most robust glass in the world. It has high thermal properties; hence, it is used for special equipment like space and satellite devices.
A key reason why many electronic devices employ glass transparent Printed Circuit Boards is their invisible wire connections, making devices attractive and increasing their value.
Except for no electrical advantages, it has no apparent detriment to manufacturers.

Ceramic, Transparent PCB is made using aluminum oxide, alumina, and magnesium oxide. During the design process of Ceramic, transparent Printed Circuit Board, many manufacturers add small amounts of fine alumina powder to resin water liquids. This process helps to increase resin hardness.
Since the conductors in the Ceramic Transparent Printed Circuit Boards are opaque, Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards Manufacturers often use transparent substrates with a solder mask based on the glass to improve their transparency between the ranges of 75% to 85%.
Ceramic Transparent Printed Circuit Boards are applicable in the following areas
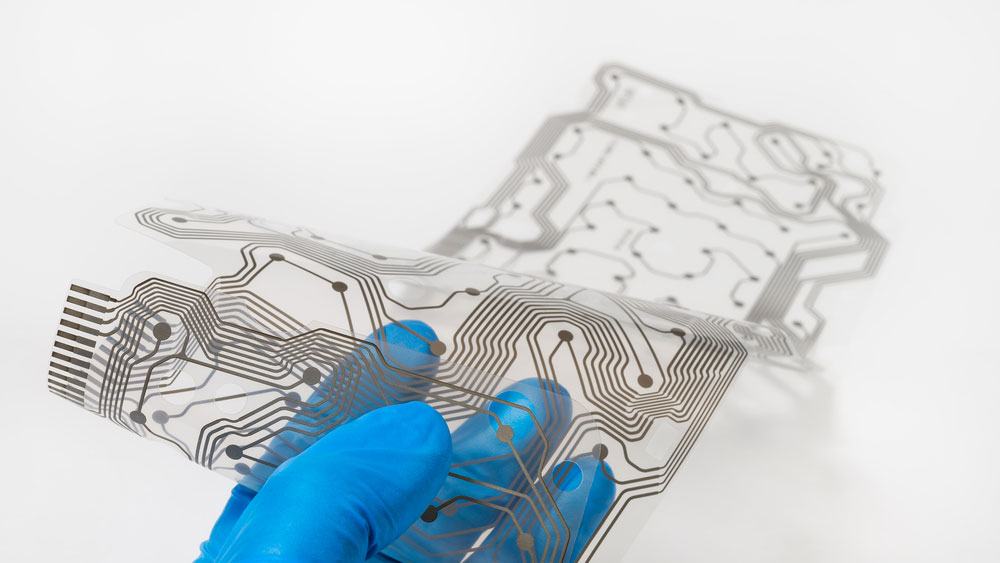
Transparent flexible PCB contains thin films that are white, light blue, transparent, light brown, or lighter colors. With PET films, manufacturers can design transparent flexible Printed Circuit Boards.
Transparent Flexible Printed Circuit Boards design requires a skilled technique that involves clamping the printed circuit between two thin films. There are flexible Printed Circuit Boards where the substrate is only transparent while the pads and conductive traces are not yet they are visible. Also, there are transparent flexible printed Circuit boards where every component is transparent, including its conductive traces.
Designing and making a transparent Printed Circuit Board is a straightforward process. Here are the required steps.
While the manufacturing steps of transparent Printed Circuit Boards are straightforward, there must be strict adherence to crucial design rules to optimize their performance.
When finding a suitable Printed Circuit Board manufacturer, there are essential tips to ensure you get the best. This guide provides ten crucial tips on getting the best Transparent Printed Circuit Board designer anywhere in the world.
A lot of revolutionary changes are happening in the PCB industries. Different kinds of Printed Circuit Boards power many electronic devices. Also, Manufacturers are using these Printed Circuit Boards to meet the design needs and requirements of these electronic devices.
The guide shows different kinds of transparent Printed Circuit Boards manufactured in the industry. Transparent Printed Circuit Boards are highly functional circuit solutions for manufacturers and consumers.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now