Introduction
The medical industry requests the highest precision, quality, and reliability of the circuit board. NextPCB is in constant work of providing our service in the healthcare market. We provide documentation to our customer, ensuring that the PCB assembly satisfy the manufacturing requirements.
This guide explains what medical PCB assembly is. It also covers why it is important and how we ensure high quality in medical electronics manufacturing.
What is Medical PCB Assembly?
Medical PCB assembly is the process of constructing a printed circuit board (PCB) for use in medical devices. The process involves mounting and soldering electrical components onto the board, such as capacitors, resistors, transistors, and integrated circuits.
The assembly process is critical for the accuracy and reliability of medical devices. The boards control how the device works, send data, and provide power to its parts. Proper PCB assembly is crucial for the safe use of medical devices. Any mistakes in assembly can cause malfunctions or harm to patients.
Experienced technicians or engineers should perform medical PCB assembly, as it is a highly specialized process. Additionally, we must test the boards to ensure that they meet the required standards and specifications.
Application of PCB Assemblies in the Medical Device Industry
The safety and well-being of patients are guaranteed by engineering electronic devices and diagnostic tools for exceptional precision, long lifespans, and reliable performance. Manufacturers integrate high-quality PCBAs into medical products to meet these requirements.
In recent years, designers have created and produced PCBAs in ways that help PCB manufacturers. This has improved the accuracy of measuring tools. It has also increased the flexibility of treatment design.
Finally, it has sped up how quickly medical staff share information. Some examples of medical technologies or equipment that have PCB include:
- Handheld monitors
- Pacemakers
- Blood Pressure Monitors
- Drug Delivery Systems
- Imaging and Diagnostic Equipment
- Body Temperature Devices
- Infusion Fluid Control
- Heart Monitors and Implants
- Flow Rate Dispension Systems
- Dental Equipment
- Digital X-ray Equipment
Medical technologies are critical and should meet extremely strict quality standards. PCB assembly processes often involve packing many connections closely together on a small surface. This helps the final assembly fit into tight spaces, as medical devices are getting lighter and smaller.
This small and dense layout requires many considerations during design and assembly. You can use your PCB assembly partner's expertise to navigate some of the factors listed below.

PCB Materials Used in Medical PCB
You'll have a wide range of choices regarding PCB materials and specifications for your medical devices and equipment. You can optimize the performance of your medical device by selecting the right PCB specifications. Here are some of the most common PCBs used in medicine. We will also look at what makes each PCB good for certain uses.
Medical PCB Material Selection Guide for High-Reliability Devices
|
Material Type
|
Key Properties & Advantages
|
Medical Applications
|
Best For
|
Compliance/Standards
|
|
Flexible PCBs
|
• Dynamic bending (500k+ cycles)
• 0.1mm thickness
• 30% weight reduction vs rigid PCBs
|
Wearable medical devices: ECG patches, glucose monitors
Endoscopic tools: Camera leads
Implantable leads
|
• Flex PCB medical applications
• Space-constrained devices
|
IPC-6013 Class 3
ISO 13485
IEC 60601
|
|
Aluminum MCPCBs
|
• Thermal conductivity: 2-5 W/mK
• Dielectric strength: 4kV
• 10X heat dissipation vs FR4
|
Surgical lighting systems
Laser treatment equipment
Medical scanning systems
|
• Thermal management medical PCBA
• High-power electronics
|
UL 94V-0 Flammability
RoHS compliant medical devices
|
|
HDI Microcircuits
|
• Microvias: 50μm diameter
• 30μm trace width
• 5μm line spacing
|
Neural implants
Hearing aids
Nano-sensor platforms
|
• Micro-coil PCB assembly
• Miniaturization in medical electronics
|
IPC-2226 Standards
Biocompatible PCB materials
|
|
Polyimide PCBs
|
• Continuous temp: -269°C to 400°C
• Chemical resistance: Acids, solvents
• 500 MPa tensile strength
|
Sterilization compatible PCBA: Autoclaved instruments
Prosthetic controllers
Deep implant electronics
|
• High-temperature applications
• Chemical exposure environments
|
ISO 10993 Biocompatibility
NASA outgassing standards
|
|
Ceramic PCBs
|
• CTE: 4-8 ppm/°C (matches silicon)
• Thermal conductivity: 24-170 W/mK
• 0.05% moisture absorption
|
MRI & CT imaging systems
RF ablation catheters
Portable X-ray generators
|
• High-frequency/high-voltage PCBs
• Thermal management critical
|
IEC 60601 EMC Compliance
UL 94V-0
|
|
Rigid-Flex PCBs
|
• Dynamic flex rating: 100k cycles
• 40% weight savings
• 500 mil bend radius
|
Surgical robots
Portable ventilators
Digital stethoscopes
|
• Rigid flex PCB medical
• Vibration-prone environments
|
IPC-6013D Class 3
MIL-P-50884
|
|
Biocompatible PEEK™
|
• 0.02% moisture absorption
• V-0 flammability
• Radiation resistance: 1000 Mrad
|
Chronic implants
• Spinal stimulators
• Cardiac rhythm leads
Dental imaging sensors
|
• PCB assembly for implantable medical devices
|
ISO 10993-5 Cytotoxicity
USP Class VI
|
|
PTFE RF Substrates
|
• Dk: 2.0-10.2 at 10GHz
• DF: 0.001-0.002
• Phase stability: ±2.5 ppm/°C
|
• Microwave ablation systems
• 5G-connected implantables
• Telemedicine devices
|
• Signal integrity medical electronics
• High-frequency designs
|
IEC 60601-1-2 EMC
IPC-6012 Class 3
|
Flexible PCBs
Flex PCB is the first choice for medical equipment. Flex PCBs are a good choice for medical devices. They are flexible and can fit in tight spaces.
Flexible aluminum PCBs
Some high-power medical devices require harder PCBs, which are unsuitable for flex PBCs. Because of their heat transfer abilities, flexible aluminum PCBs are ideal for high-power applications. Surgical lighting and scanning are some of the most popular applications for these boards.
PCB microcircuits:
A flexible PCB microcircuit might also be an option to consider. Moreover, PCB microcircuits offer greater performance than flex PCBs, which is what makes them so unique. Microcircuits on PCBs are commonly present in small medical devices, such as wearable technology, industrial sensor, etc.
Polyimide PCB material
The polyimide base material is often one of the best choices when designing PCBs. The tensile strength and flexibility of polyimide PCB materials are excellent. Medical devices like prosthetics and implants can benefit from these materials. They are exceptionally durable, stable in heat, and resistant to chemicals.
Ceramic PCBs
Ceramic PCBs
have a low thermal expansion coefficient and high thermal conductivity. This makes them a great choice for medical device makers.
These PCBs can work in extremely high temperatures. They also perform well at high frequencies. They are easy to use for high-density tracing and are resistant to chemicals.
Rigid-flex PCBs
A flex circuit and rigid-flex PCB can make the PCB durable and strong. The conductors sit between rigid and flexible materials to connect the flexible materials with other layers. Rigid boards are more durable and offer better design options. They are lighter and smaller than flex boards.
Material Performance Rankings
|
Characteristic
|
Best Material
|
Worst Material
|
Performance Gap
|
|
Flex Cycle Life
|
Polyimide Flex PCB (>500k cycles)
|
FR4 (<10k)
|
50X
|
|
Thermal Conductivity
|
Aluminum Nitride (180 W/mK)
|
Standard FR4 (0.3 W/mK)
|
600X
|
|
Chemical Resistance
|
PEEK™ (pH 0-14 stability)
|
Paper-Phenolic
|
Infinite
|
|
High-Frequency Loss
|
Rogers RO3003™ (tan δ 0.001)
|
G-10 FR4 (0.02)
|
20X
|
Basic Considerations for Medical PCB Assembly
Medical PCBs are designed and assembled by following some strict guidelines. For any devices or equipment used in the medical domain, designers should consider the following factors:
Safety is one of the important considerations in the design and manufacturing of PCBs. Patients use medical devices directly. Thus, any circuitry malfunctions are extremely dangerous and can be life-threatening. Therefore, designers make well-engineered medical devices and their components even when exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
A PCB fabricator can help you design high-reliability PCBs. They can work with you to reduce safety risks and solve specific problems.
Learn NextPCB's PCB Assembly Services
Medical devices must comply with strict standards depending on their function and environment. Ensuring your device complies with all regulatory requirements requires working with a PCB manufacturer familiar with these standards. The medical industry has strict rules for tracking components. A good PCB manufacturer can give detailed records of testing and inspection.
For medical practitioners and other users to enjoy your product, you must balance functionality and usability. Several physical attributes and specialized designs make medical devices practical and easy to use. Your device can deliver maximum value and utility when you choose a PCB manufacturer that incorporates these design considerations.
Electronic devices cannot function without PCBs, which is why they must be able to work without fault. A PCB assembly can be highly prone to corrosion. This happens when manufacturers and solderers leave behind residues, like inorganic salts and acids, during the process. As a result, your electrical device may end its useful life without warning because of corrosion.
In addition to improving PCB assembly reliability, contaminant removal enhances the reliability of medical devices. PCB manufacturers need to ensure that their products are clean.

PCB Assembly Challenges in Medical Device Industry
Medical devices can face various challenges while constructing and designing products. Some of the common challenges faced in the medical industry include the following:
Manufacturing tools and equipment are subject to many regulations in the medical industry. Complying with these standards protects staff and patients from unsafe, unreliable, and untraceable products. Companies also have difficulty getting their products approved for marketing because of stringent regulations. Complying with the relevant standards is mandatory for all components, including PCBs.
Medical devices offer reliable performance. It ensures that equipment and devices consistently perform according to their design and specifications.
Medical device development and production are similar to other manufacturing projects in that they must adhere to a budget. To maintain performance and regulatory compliance at a reasonable cost, manufacturers must find a way to balance the two.
Size is one of the challenges in medical PCB. Medical PCB should be smaller in size to fit medical devices. This trend is increasing with the more advanced technologies and electronics. A good PCB manufacturer can skillfully create smaller PCBs that deliver excellent performance.
Since PCB-equipped medical equipment is often lifesaving, it must be reliable. Medical devices should work in extreme conditions like liquid, shocks, temperature, etc. Although working in such a harsh environment, these PCBs should provide reliable and effective results.
Technologies for Medical PCB Assembly
Types of Medical Devices PCB
Wearable Technology
NextPCB designs and manufactures flexible PCB for smart wearable devices. By using a flexible PCB, this device combines user-friendliness, connectivity, and a high level of functionality. The ergonomic design of the device met the expectation of users.
Characteristics
- Flex PCB has the bending property that reduces the size and cost of manufacturing.
- With the flex PCB, you can easily mold the device into various shapes.
- The designing and working with flex PCB is user-friendly.
- Diagnostic Device Technology
Instant testing kits for blood tests and diabetes are demanding in the market. Compact-sized PCBs, flexible PCBs, and multilayer PCBs provide small size, compactness, lightweight design, and high-speed functionality. Thus, we provide you with a durable PCB for wireless Diagnostic devices. They ensures signal integrity with less heat and power consumption.
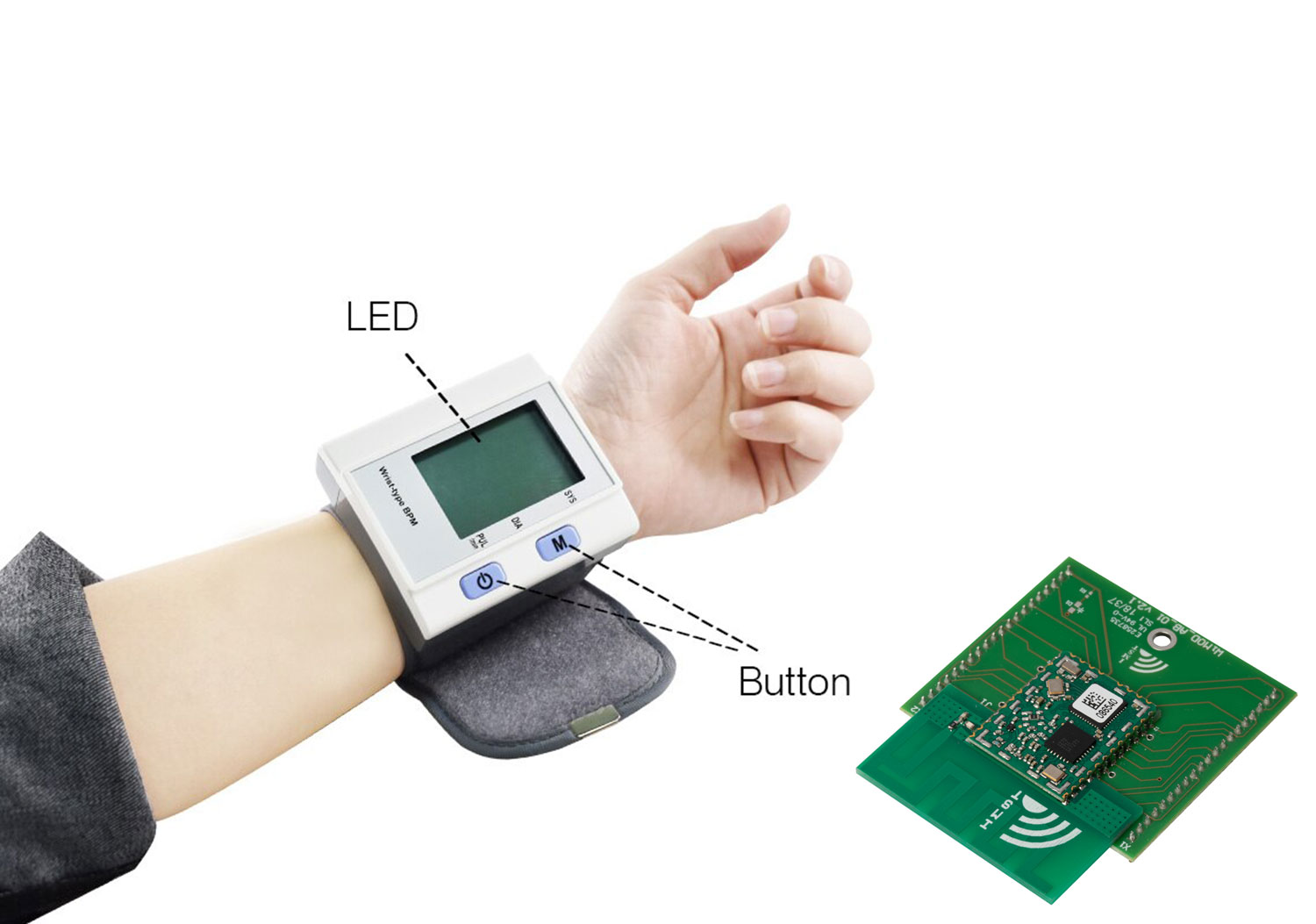

Electrotherapy Equipment
Some medical devices, like electrotherapy, deal with human life. Thus, it's very important to keep their design priority. These devices are of various formats and therefore require various types of PCBs. Moreover, some may use single layered while others may use multilayer PCBs. At, NextPCB, we designed single to multi-layered PCBs. Our expertise can help you with any challenges in PCB design.
Single Layered PCB
Single-Layered PCB is easy to design and consider. Besides, they are cost-effective and don't require any complex components.
Characteristics
- Provide resistance against bending and breaking of the circuit
- Perfect to use in sensor devices
- Cost efficient design
- Time for troubleshooting the fault is less.
- They are perfect for simple analog and digital circuits.
Multi-layer PCB
It consists of 3 layers of conductive materials. The PCB reduces the size of the device and finally optimizes power consumption.
Characteristics of Multi-layer PCB
- High-quality product
- Improve durability
- Small laser drilling, hole drilling
- Greater capacity due to high-density assemblies
- Minimal impedance that results to high quality
Design and Fabricate the Medical PCB
Schematic Diagram
The schematic design is the foremost step in the design and manufacturing process. The system collects all the required information from the user. Some of the reports include PCB types, application of PCB, materials, and power requirements of PCB. These accurate designs create the initial design of the medical PCB.
Layout
A PCB layout is followed by a schematic design. The required details of the project are considered, and further work is done.
Recommend reading: PCB Layout Design Rules: The Ultimate Guideline Is Here
Crucial factors
The design process of a Medical PCB requires consideration of several critical factors. Several essential elements go into selecting pins, including the split planes, the sequencing, and the number of pins.
Split Power Properly
This stage of the design process involves splitting power to reduce noise and crosstalk on the board. Diversifying power properly is important to achieve effective results.
Allow Multiple Layers
Layering the PCB base multiple times is necessary to reduce noise and SNR. Medical PCBs with multiple layers are also more reliable and perform better.
Review BOM (BOM) List
The next step is to review the medical PCB bill of material BOM. Medical PCB Bills of Material contain all the parts and materials.
Check Components
In this stage, manufacturers check the Medical PCB parts thoroughly to ensure they meet design requirements.
Prepare and Verify Alternative Component Lists
Occasionally, certain PCB components fail to meet design requirements or fail to function properly. An additional list of components is prepared beforehand to deal with this issue. By doing this, the designing process can be speed up.
Make a Drawing for the Assembly
Assembling medical PCBs is a complex process. Additionally, Medical PCBs need to be extremely accurate since they are used in a sensitive medical field. PCB design and assembly should be error-free. An assembly process drawing is created and followed diligently to ensure PCB assembly accuracy.
Show Test Points in the Design
The human body requires precision and accuracy when it comes to medical devices. It also requires accurate, error-free Medical PCBs to manufacture these devices. A PCB should include all possible test points to achieve this.

Assembling Medical PCB
PCB assembling requires consideration of several important factors. Circuit boards, PCB parts, and their functions are all vital factors to consider.
Before assembly, you need some essential tools to help you. Testing equipment, soldering machines, and SMT equipment are some of the critical assembling tools. Some other materials include solder wire and paste.
The medical field is extremely sensitive, so conducting a design for manufacturability test prior to assembly is essential. During the design for manufacture test, the team identifies and corrects any design challenges before starting actual assembly. After the assembly of the medical board, DFM's primary objective is to ensure that it functions properly. Some of the assembling processes for the medical PCB are as follows:
Solder Paste Stencilling
Assembly begins with stenciling the solder paste. This board has a stencil covering it, leaving only the part where a component will mount. You can then apply solder paste only where you will mount components.
A mechanical fixture holds the board and solder stencil. Technicians then use a solder paste applicator to apply the paste at designated locations. Workers coat all exposed areas uniformly with solder paste. The solder past remains at the desired place after removing the stencil.
Pick and Place
A medical PCB is mounted accurately here with its various electronic components. Manufacturers use an assembly robot to manufacture medical PCBs because of the high accuracy required. Robots pick up and place surface-mounted devices on boards. The mounting device precisely places solder paste on the components.
Soldering Reflow
Solder overflow ensures that the joints between components and boards are strong. The conveyer belt moves the board through the large reflow oven. Next, with the heat of 2500℃, the solder paste melts. Then, the medical PCB passes through the cooler, solidifying the paste and forming the joints between the board and the parts.
Inspection and Quality Control
The assembled medical PCB undergoes inspection to identify any flaws or connectivity issues. Technicians then correct any problems that may have occurred during the reflow process. The board performs manual checks, automatic optical inspections, and X-ray inspections, among other inspections.
Last Inspection and Functionality Test
Medical PCB assembly ends with the inspection and testing of the manufactured board. The board is experiencing a rigorous functionality test in this instance. This step ensures it performs as needed and complies with the high standards of the medical industry.
Cleaning the board then eliminates oil, flux, and other debris after all the examination and approvement. This makes the medical board sterile and suitable for producing medical devices. Medical PCBs often require specialized testing. The specific medical device determines the type of testing required for the PCB.

Tips to Choose the Right Medical PCB Assembler
In the medical field, well-designed PCBs are essential for supporting life-saving procedures and enhancing patient care. Their design and assembly demand specialized expertise and strict compliance with quality, safety, and hygiene standards.
A skilled PCBA assembler who understands the unique challenges of medical applications can help manufacturers meet these stringent requirements. When choosing a PCB assembler, look for the following key qualities:
Vital to know that your manufacturer should have the expertise and knowledge to meet the standard of the project. Your manufacturer should have experience in manufacturing and designing PCBs similar to your project applications. During the execution and planning stages, knowledges gained from the experience and the expertise can help to avoid mistakes.
Turnkey PCB assembly suppliers like NextPCB offer numerous advantages for medical device manufacturers. Working with a single manufacturer throughout the entire process—from prototyping and production to final delivery—simplifies communication and project coordination.
This streamlined approach makes it easier to address questions and concerns, and provides better control over the project. As a result, it often leads to higher product quality and faster fulfillment and delivery times.
If you need an instant online quote, please feel free to visit us at: PCB Assembly Quote
- Sufficient Resources and Capacities
Your PCB manufacturer and assembler should have the necessary equipment to accommodate your production requirements, including volume, design, and materials.
Why NextPCB for Your Medical PCB Needs?
NextPCB is a Contract Manufacturer of PCB and PCB-related services. We can produce reliable and durable PCB solutions that meet technical specifications and quality standards. Below is a list of certifications reflecting our capability to deliver PCB assembly services for medical applications as well as other industries:
- ISO 9001:2015 quality certification
- ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System (EMS)
- IATF 16949:2016 International Standard for Automotive Quality Management System
- REACH, Regulation concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals
- RoHS, Restriction of Harza Substances
- UL E469747
- Detailed information about NextPCB's Quality Certifications and Test Reports
NextPCB is the Chinese PCB manufacturer and assembler that offers full turnkey product assembly capabilities, board fabrication, testing, serialization, component sourcing, etc.
FAQs:
Q: What is medical device assembly?
Medical device assembly is the process of combining various components, such as sensors, circuits, and mechanical parts, to create a fully functional medical device, ensuring it meets quality and safety standards.
Q: What is a PCB in healthcare?
Medical device assembly is the process of combining various components, such as sensors, circuits, and mechanical parts, to create a fully functional medical device, ensuring it meets quality and safety standards.
Q: What is an assembly in medical terms?
In medical terms, assembly refers to the process of putting together the parts of a medical device, such as circuits and mechanical components, to create a working product for patient care.
Conclusion
Medical PCBs are becoming popular in diagnostic devices, bioanalysis equipment, and laboratory devices. In the medical industry, it plays a vital role. Thus, the assembled process of medical PCB is of high standards. Almost all medical devices use this PCB, and the manufacturer's design and assembly follow separate medical rules and standards.
If you require further assistance, please feel free to contact us at: support@nextpcb.com












