
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
PCB: the full name is printed circuit board, which can be divided into a single panel, double-sided board, and multi-layer board. It is the support of electronic components and the carrier for the connection of electronic components. Because it is made by electronic printing, it is also called a printed circuit board. It is an important assistant to promote the development of a 5g commercial landing, automotive electrification, and intelligent equipment.
Most PCBs for simple electronic devices are simple and consist of only one layer. More complex hardware (such as a computer graphics card or motherboard) can have multiple layers, sometimes up to twelve.
Although PCBs are most often associated with computers, they can be found in many other electronic devices, such as TVs, radios, digital cameras and mobile phones. In addition to being used in consumer electronics and computers, different types of PCBs are also used in many other fields, including:
Today, electronics are denser and consume less power than previous generations, enabling the testing of exciting new medical technologies. Most medical devices use high-density PCBs, which are used to create the smallest and most dense designs. Due to the need for small size and lightweight, this helps to alleviate some of the unique limitations associated with developing devices in the medical field. From small devices such as pacemakers to large devices such as x-ray devices or cat scanners, PCB has been used in all fields.
As LED-based lighting solutions are popular due to their low power consumption and high efficiency, so is the aluminum PCB used to manufacture them. These PCBs are used as heat sinks, allowing a higher level of heat transfer than standard PCBs. These same aluminum-backed PCBs form the basis for high lumen LED applications and basic lighting solutions.
Both automotive and aerospace industries use flexible PCBs, which are designed to withstand the high vibration environment common in both fields. Depending on the specifications and design, they can also be very lightweight, which is necessary for manufacturing parts for the transportation industry. They can also accommodate narrow spaces that may exist in these applications, such as inside the instrument panel or behind the instruments on the instrument panel.
PCB is usually used in high-power industrial machinery. Where the current one-ounce copper PCB can not meet the requirements, thicker copper PCB can be used. Advantages of thicker copper PCB include motor controller, high current battery charger, and industrial load tester.
Different types of circuit boards, each with its own specific manufacturing specifications, material types, and uses. PCB types can be divided into single-layer PCB, double-layer PCB, multi-layer PCB, hard PCB, high-frequency PCB, flexible PCB, hard flexible PCB, aluminum backplane, and other types. Let's explain them in detail.
Single-layer or single-sided PCB is a PCB made of a single-layer substrate or substrate. One side of the base material is coated with a thin layer of metal. Because the most common function of copper as a conductor is how to use it. Once a copper-based coating is applied, a protective solder mask is usually applied, followed by a final screen printing to mark all elements on the board. Single-layer / single-sided PCB is easy to design and manufacture because it only solders various circuits and components to one side. This popularity means they can be purchased at a low price, especially for large orders. Low cost, high volume models mean they are commonly used in a variety of applications, including calculators, cameras, radios, stereo devices, solid-state drives, printers, and power supplies.
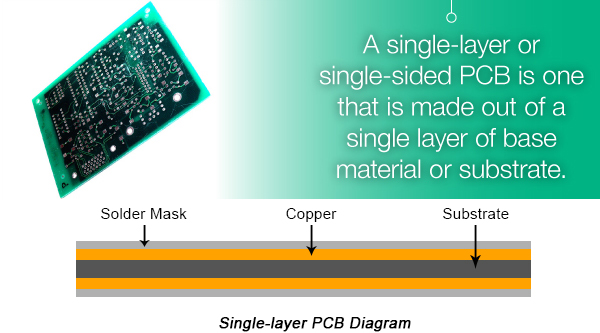
Let's conclude the features of single layer:
The substrate of double-layer or double-sided PCB is coated with a thin layer of conductive metal (such as copper) on both sides of the board. Through the hole of the board, the circuit on one side of the board can be connected to the circuit on the other side. The circuits and components of a double-layer PCB are usually connected in one of two ways: via or surface mount. Through-hole connection means that a thin wire called a lead wire is passed through the hole, and then each end of the lead wire is welded to the correct assembly.
Surface mount PCB does not use wires as connectors. Instead, many small leads are directly soldered to the board, which means that the board itself is used as the routing surface for different components. In this way, less space can be used to complete the circuit, and more space can be released for the board to complete more functions, usually at a higher speed and lighter weight than the through-hole board allows. Dual-sided PCBs are commonly used in applications that require moderately complex circuits, such as industrial controls, power supplies, instrumentation, HVAC systems, LED lighting, automotive dashboards, amplifiers, and vending machines.
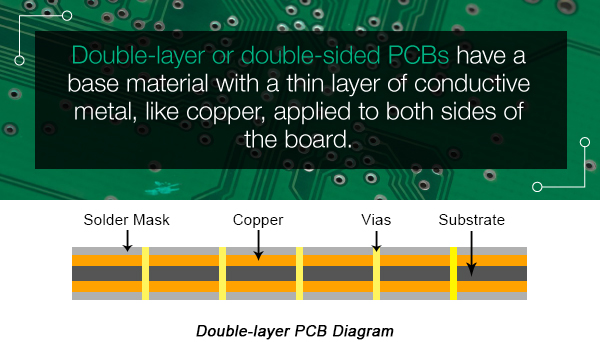
Let's conclude the features of the double-layer layer:
A multilayer PCB consists of a series of three or more double-layer PCBs. The panels are then held together with special glue and sandwiched between the insulation sheets to ensure that the excess heat does not melt any components. The size of Multilayer PCB varies from four layers to ten or twelve layers. The largest Multilayer PCB thickness ever is 50 layers. Through multilayer printed circuit board, designers can carry out very thick and complex design, which is suitable for various complex electrical tasks. Applications that multilayer PCB will benefit from include file servers, data storage, GPS technology, satellite systems, weather analysis, and medical devices.
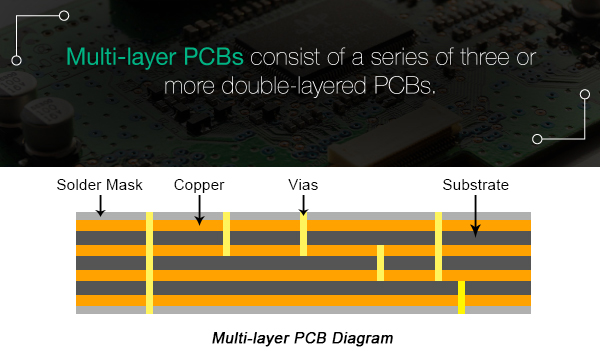
Let's conclude the features of multilayer PCB:
Rigid PCB is made of solid substrate material, which can prevent the circuit board from twisting. The most common example of a rigid PCB is a computer motherboard. The motherboard is a multilayer PCB designed to distribute power while allowing communication between all many parts of the computer (such as CPU, GPU, and RAM). Hard PCBs may constitute the largest number of PCBs produced. These PCBs can be used anywhere where the PCB itself needs to be set to a shape and remain in this state for the rest of the life of the device. Rigid PCB can be simple single-layer PCB to eight or ten layer Multilayer PCB. All rigid PCBs have single-layer, double-layer or multi-layer structures, so they share the same application.
Flexible printed circuit boards are made of flexible and mobile materials, such as plastic. Like rigid PCB, flexible PCB has single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer forms. Because they need to be printed on flexible materials, the manufacturing cost of a flexible printed circuit board is higher.
Compared with rigid PCB, flexible PCB has many advantages. The most prominent of these advantages is their flexibility. This means they can fold over the edges and wrap around the corners. Their flexibility can save cost and weight because a single flexible PCB can be used to cover areas that may require multiple rigid PCBs. Flexible PCBs can also be used in areas that may be exposed to environmental hazards. For this purpose, they are only made of waterproof, shockproof, corrosion-resistant, or high-temperature oil-resistant materials.
Hard and flexible circuits combine the best of both worlds of the two most important PCB boards. The rigid-flexible board is composed of a multi-layer flexible PCB, which is attached to multiple rigid PCB layers. Rigid flexible PCBs are most commonly used in the most important applications of space or weight, including mobile phones, digital cameras, pacemakers, and cars.
Rigid-flexible PCB has many advantages compared with rigid or flexible PCB:
High Frequecy PCB
High-frequency PCB refers to the general PCB design elements, rather than the PCB structure type of previous models. High-frequency PCB is designed to transmit signals at 1 GHz frequency. Poly (ethylene oxide) (PPO) and polytetrafluoroethylene (FR4) laminates are commonly used as high-frequency strengthening materials. Teflon is the most expensive option because of its small and stable dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, and low overall water absorption. When selecting high-frequency PCB and its corresponding PCB connectors, many aspects need to be considered, including dielectric constant (DK), dissipation, loss, and dielectric thickness. The most important is the DK of the material in question. Materials with high permittivity change possibility usually have impedance change, which will destroy the harmonics of digital signal and lead to the overall loss of digital signal integrity, which is one of the things that high-frequency PCB aims to prevent. Other considerations when selecting the type of board and PC connector to use when designing high-frequency PCB include:
The design of aluminum PCB is almost the same as that of copper-backed PCB. However, instead of fiberglass commonly used in most PCB types, aluminum or copper substrates are used.
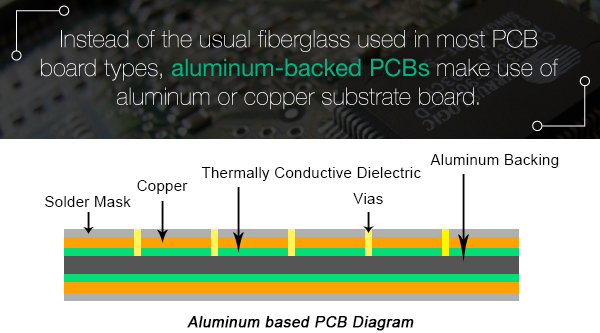
The aluminum backing has an insulating material, which is designed to have a low thermal resistance, which means less heat is transferred from the insulating material to the backing. After the insulating layer is applied, a copper circuit layer with a thickness of 1 to 10 ounces will be applied. Aluminum backed printed circuit board has many advantages over glass fiber backed printed circuit board, including:
All of these advantages make aluminum PCB an excellent choice for applications requiring high power output within very strict tolerances, including traffic lights, automotive lighting, power supplies, motor controllers, and high current circuits. Aluminum-backed PCBs can also be used in applications requiring high mechanical stability or where PCBs may withstand high levels of mechanical stress. They are less affected by thermal expansion and have a longer life than fiberglass.
NextPCB runs three factories specialized in PCB Prototype, PCB Mass Production, and PCB Assembly, equipped with AOI, X-Ray Testing & Multiple functional testing. We could provide quick-turn service without a broker. And you could get high-quality PCB and PCB assembly at a competitive price.
PCB Assembly Quote Quickly From NextPCB
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: |
Thickness: |
|
|
|