
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comIn designing and producing a printed circuit board (PCB), one of the crucial decisions is choosing the type and style of components. In the past, the common choice was to insert components into holes drilled into the PCB. However, in recent years, there has been a shift towards a newer method that eliminates the need for drilling holes. This article provides a brief explanation of Through Hole Technology and its difference from SMT technology.
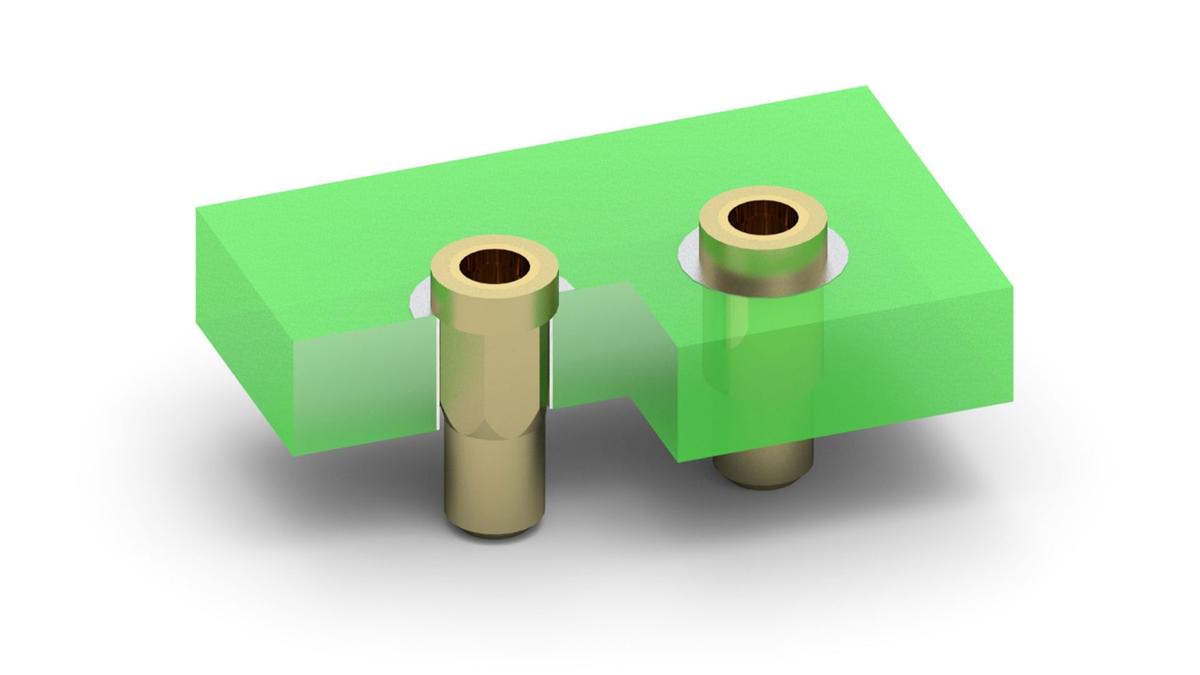
Through Hole Technology (THT) is a method of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) by inserting the leads of the component into drilled holes in the PCB and soldering the leads to the pads on the other side. This creates a permanent connection between the component and the board.
The process of THT typically involves drilling holes in the PCB, inserting the component leads into the holes, and then soldering the leads to the pads on the other side of the board. Thus, it creates a strong mechanical and electrical connection between the component and the board, making THT an ideal choice for high-reliability and durability applications.
One of the key benefits of THT is its ability to handle high-power components, making it an ideal choice for power electronics applications. THT components can also handle high temperatures and vibrations, making it an ideal choice for harsh environments. The process of THT is also relatively straightforward, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturers.
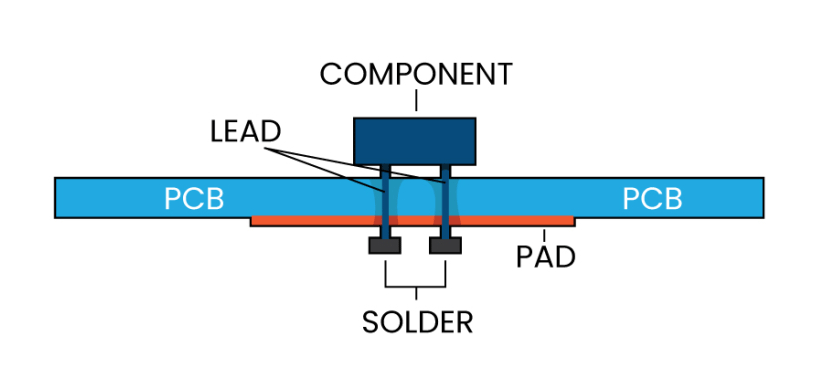
The working of Through Hole (TH) Technology involves inserting the leads of the components into drilled holes in the printed circuit board (PCB) and soldering the leads to the pads on the other side of the board. This creates a permanent connection between the component and the board. The process of THT typically involves the following steps:
Drilling Holes: Holes are drilled in the PCB in the desired pattern, allowing the leads of the components to be inserted.
Inserting Components: The leads of the components are inserted into the drilled holes and held in place using clamps or retaining clips.
Soldering: The leads of the components are then soldered to the pads on the other side of the board, creating a permanent mechanical and electrical connection between the component and the board.
Inspecting: The soldered connections are then inspected for any defects, such as cold solder joints, to ensure the reliability and quality of the connections.
Cleaning: The assembled board is then cleaned to remove any residual flux or other contaminants that may affect the performance of the components.
Final Testing: The assembled board is then tested to ensure that all components function correctly and that the connections between the components and the board are reliable.
Through-hole technology provides a durable and reliable connection between the components and the board. It then makes it an ideal choice for applications that required high reliability and longevity.
Through Hole (TH) Technology has several advantages in electronic manufacturing, including:
While through-hole technology has been widely used in the past, it has some disadvantages compared to newer assembly methods like surface mount technology (SMT). Here are some of the disadvantages of through-hole technology:
Through Hole (TH) Technology has a wide range of applications, including:
The decision to use through-hole technology (THT) or surface-mount technology (SMT) will depend on several factors, including:
The use of THT is for more significant components that are difficult to mount directly onto the surface of the printed circuit board (PCB).
SMT components have a finer lead pitch (the distance between leads) than THT components, making SMT more suitable for high-density designs.
THT components require more time and manual labor, while SMT's assembly process is quicker with automated equipment.
SMT is an automated process while THT is a manual process. The SMT process is much faster than using pick-and-place machines.
THT components are often easier to find and are generally less expensive than SMT components. However, SMT components may be the only option for many newer, high-density designs.
THT components are generally more reliable than SMT components due to their larger size and stronger mechanical connections. However, manufacturers can design SMT components with enhanced reliability features.
Finally, THT components can be easier to work with in circuit board design. They do not require the same level of precision as SMT components.
| Parameters | TH Technology | SMT Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Board Space | Comparatively larger | Smaller Board Size |
| Soldering | Manually or automatically | Automated Soldering |
| Pads and Vias | No pads and vias | Consists of pads and vias |
| Stencils | Doesn't use stencils | Use stencils |
| Components | Mounted on only one side | Mounted on both sides |
Through-hole technology has been in use for several decades with a proven track record of reliability and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, it is facing increasing competition from Surface Mount Technology (SMT). It offers several advantages, such as higher component density and smaller size. This makes it well-suited for miniaturization and other advanced applications.
TH technology will likely remain viable for specific electronic applications, particularly those requiring high durability, robustness, and reliability. Additionally, TH technology has a lower entry cost than SMT, making it an attractive option for smaller companies and startups.
Thus, through-hole technology (THT) is an older method of attaching components to a printed circuit board (PCB). It inserts leads into plated through holes and solders them in place. However, surface-mount technology (SMT) has replaced it in high-density designs. This is because of its faster assembly time, improved automation, and finer lead pitch.
Apart from this, the choice between THT and SMT will depend on the specific requirements of a project, including cost, size, performance, and reliability.
Working with a professional electronics manufacturer is essential to determine the best solution for your needs. A professional electronics manufacturer, NextPCB can help you determine the best solution for your needs. Feel free to contact us and you can request a quote to know more about our services.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now