
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comEvery electronic product requires a circuit. Overloading a circuit with current or electrical issues can damage it, however. If you're seeking a solution to safeguard your circuits, you've come to the right place. Various factors, such as improper connections, incorrect wiring, or human mistakes, can lead to a current overflow within a circuit. Since it's impossible to foresee when this might happen, it's wise to be prepared for such occurrences. A fuse is all you need for protection. This article will guide you through all types of fuses, their diverse uses, and how to select the appropriate one.
In this article,
Fuses serve as critical safety devices designed to protect home appliances, such as televisions, refrigerators, and computers, from high-voltage damage. Composed of a thin metal strip, a fuse melts and disconnects the circuit from the power supply when it detects excessive current flow. Fuses also function as circuit breakers or stabilizers, shielding devices from potential harm. Available in various types, features, and designs, fuse strips typically consist of aluminum, copper, or zinc and must be connected in series with the circuit to guard against overcurrent.
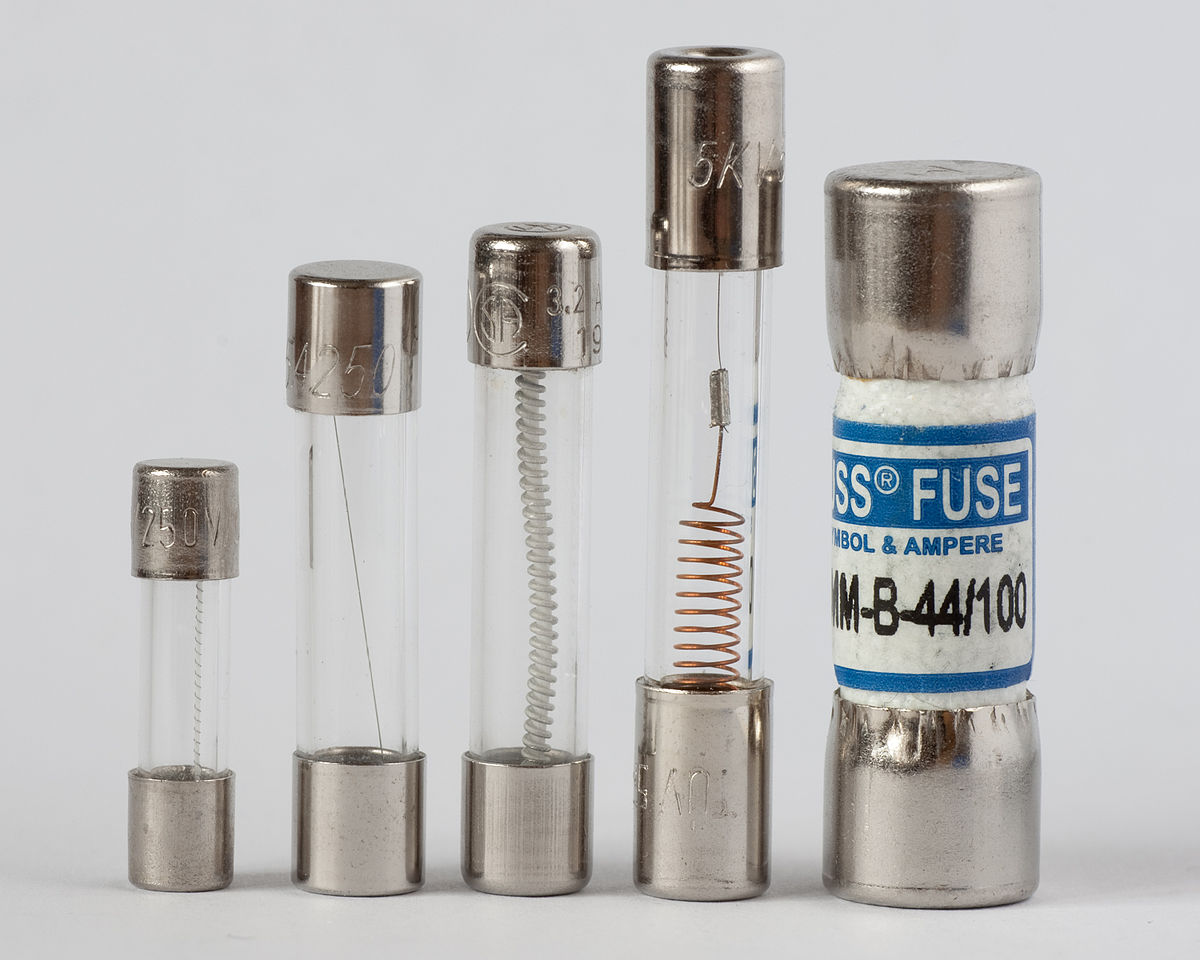

A fuse's primary purpose is circuit safety, acting as an electrical safety device that stops current flow through components when it melts due to an overflow of current. Fuses should always be connected in series with the components being protected. When a fuse blows, it opens the entire circuit, but if connected in one branch of a parallel circuit, it won't impact the current flow in other branches.
To minimize hazards associated with wire burning and electric arc blasts during severe overcurrents, manufacturers encase fuse wires within a protective sheath. Fuses come in various sizes and shapes, each designed to safeguard electronic devices with specific electrical parameters, such as operating current, speed, time, operating voltage, and fuse element melts.
Fuses play an essential role in protecting electronic devices from excessive currents. Here let’s explore various types of fuses, their unique features, and applications.

DC fuses are designed specifically for direct current (DC) circuits. These fuses are essential in safeguarding devices like solar panels or battery-powered electronics. (Image)

AC fuses protect alternating current (AC) circuits commonly found in homes and businesses. These fuses keep appliances like air conditioners and refrigerators safe. (Image). These fuses exhibit greater resistance to electric arcs upon blowing compared to DC fuses and are better suited for use with standard voltage power sources.
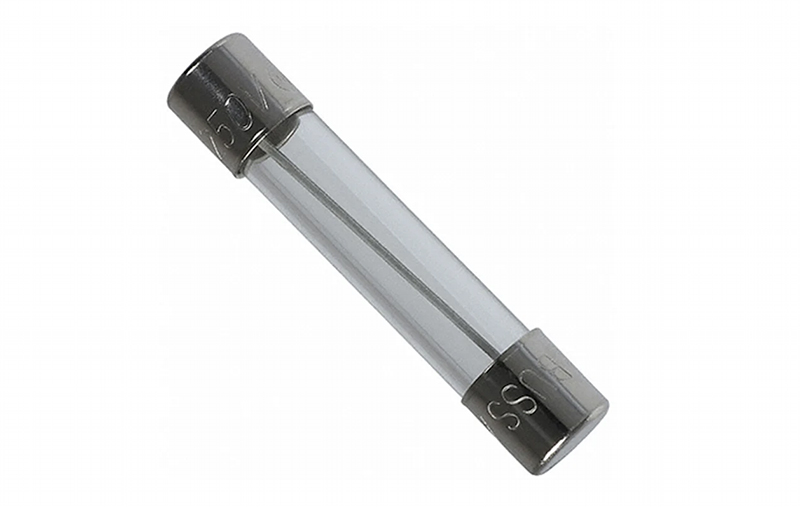

Cartridge fuses contain a metal wire enclosed within a cylindrical body. They offer reliable protection for low-voltage circuits and come in various sizes.
High voltage fuses secure circuits with large electrical loads, such as power transformers and transmission lines. They are robust and capable of handling extreme currents.
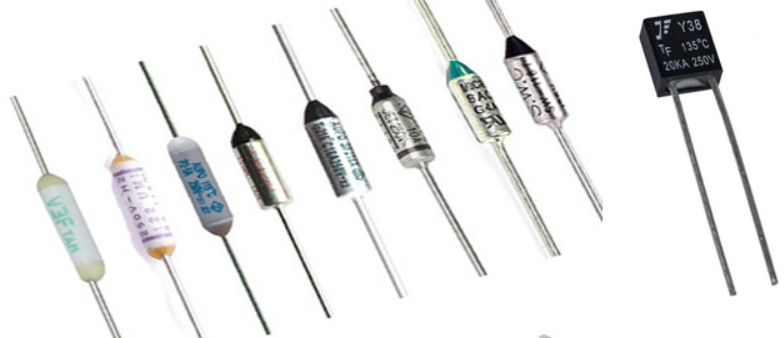
Thermal fuses protect devices from overheating. They're commonly found in appliances like coffee makers and hairdryers. Once triggered, these fuses must be replaced.
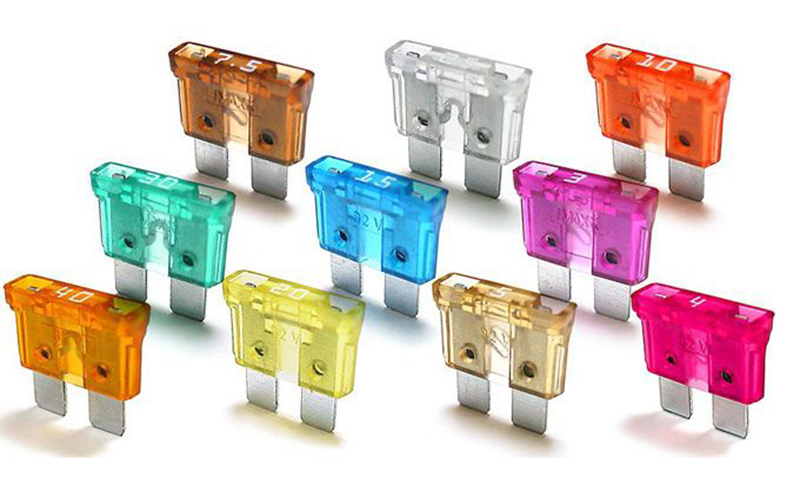
Automotive fuses, including blade and bolted-type fuses, safeguard vehicle circuits from overcurrent. They are compact, easy to replace, and color-coded for different amperage ratings.
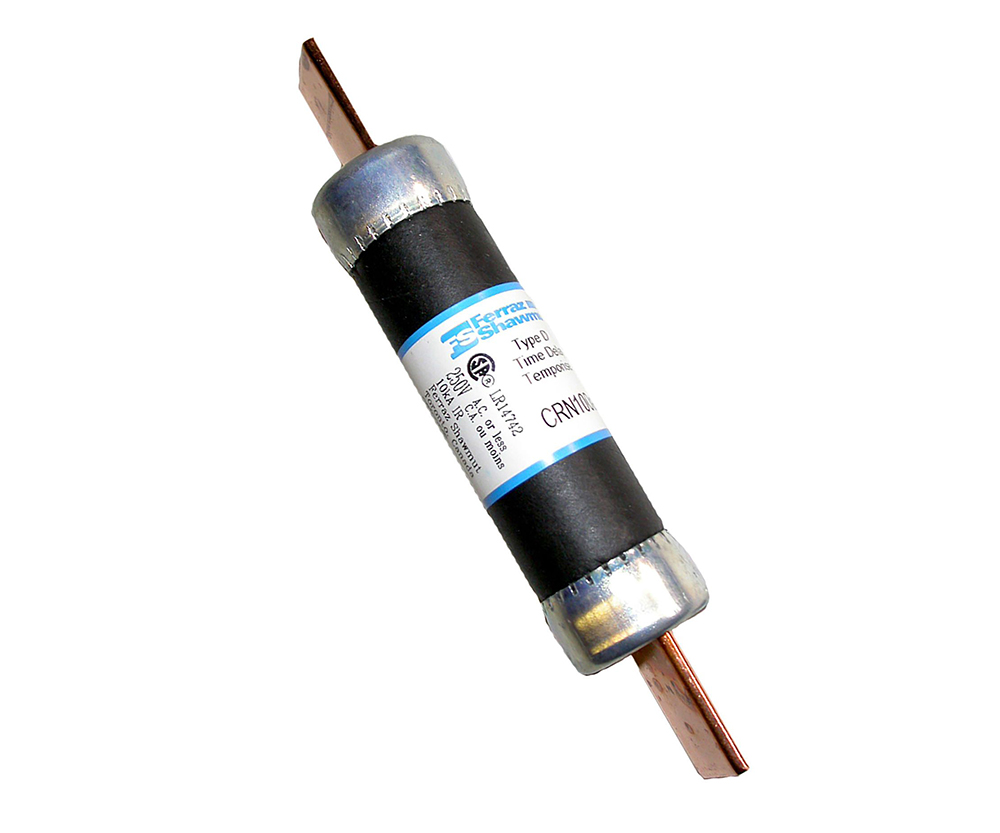

D-type cartridge fuses offer a high level of protection and can withstand substantial currents. They are used in heavy-duty electrical systems.
Rewireable fuses allow users to replace the fuse wire when blown. While less precise than other fuses, they are cost-effective and reusable.
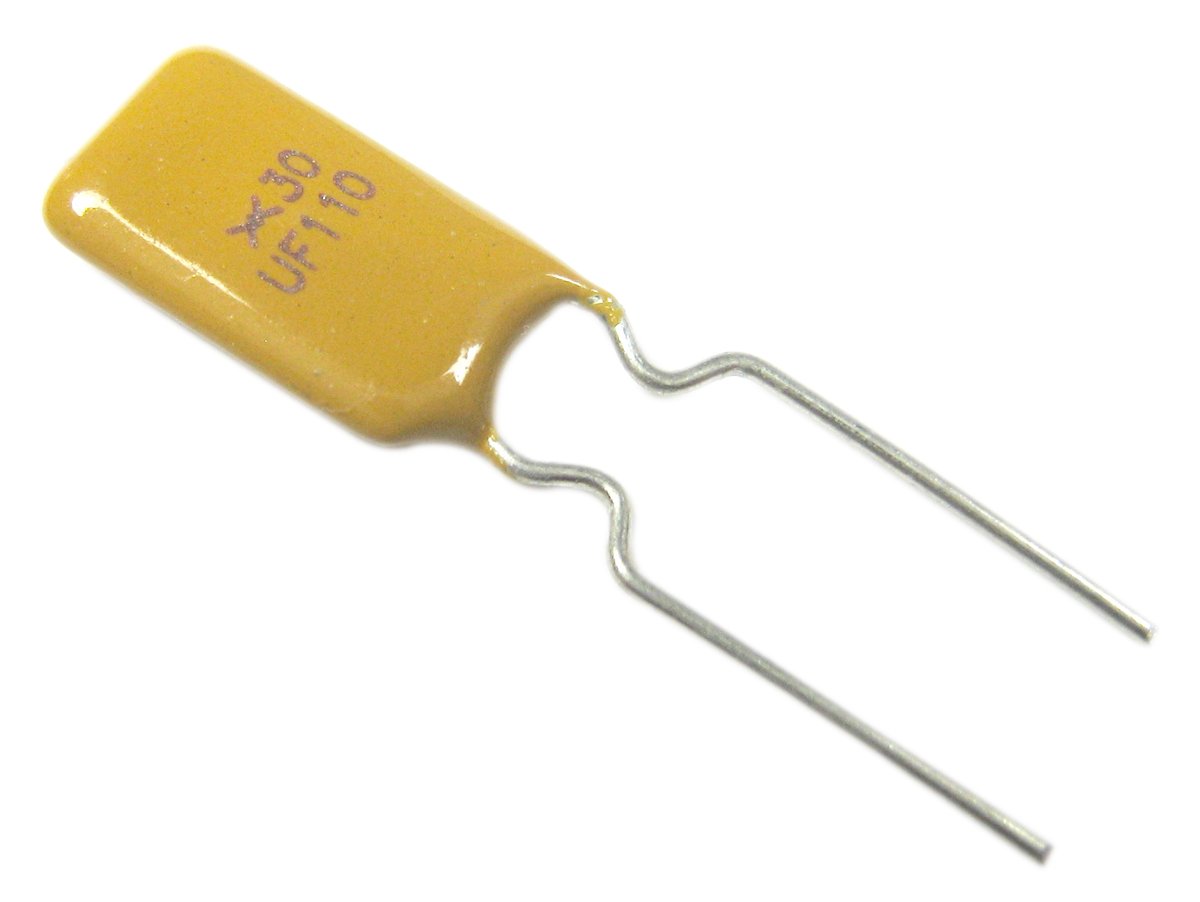
Resettable fuses, or PTCs (Positive Temperature Coefficient), automatically reset after cooling down. They are often found in computers and other sensitive electronics.
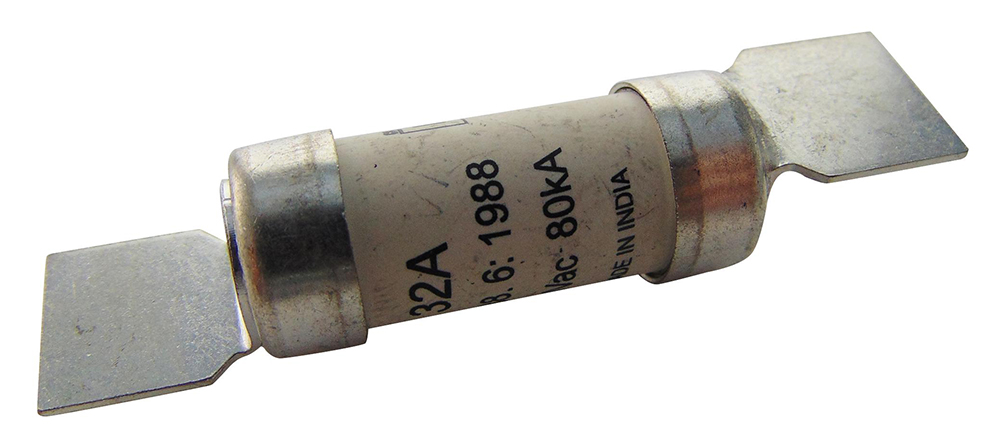

HRC fuses, or link-type cartridge fuses, can handle high currents and provide excellent protection in industrial settings. (Image)
Low voltage fuses protect circuits with lower voltage levels, such as home appliances and lighting systems. They come in various designs to suit different applications.
Drop-out fuses disconnect when excessive current flows, "dropping out" the fuse from its holder. They are typically found in electrical distribution systems.
Striker fuses feature a built-in indicator that triggers when the fuse blows, making it easy to identify and replace. They are commonly used in industrial applications.
Switch fuses are the combination of a fuse and a switch. It helps in easy circuit isolation and protection. They are often found in commercial and industrial environments.
Time-delay fuses provide a short buffer before activating. It helps to pass the temporary current surges without interruption. They are ideal for motors and transformers.
Thus, understanding the different types of fuses and their applications is crucial for safeguarding your electronic devices.
Understanding the characteristics of fuses is essential for effective circuit protection. Below are the critical features that set fuses apart and how they impact their performance.
A fuse's current rating indicates the maximum current it can carry without blowing. It's essential to choose a fuse with a slightly higher rating than the circuit's normal operating current for optimal protection.
The voltage rating signifies the highest voltage a fuse can safely interrupt. Selecting a fuse with a voltage rating suitable for your application is crucial to ensure effective protection.
Breaking capacity refers to a fuse's ability to break or interrupt a specific current without causing damage. Higher breaking capacities offer better protection against electrical faults.
Operating characteristics describe how a fuse responds to different current levels. Time-delay fuses, for example, tolerate brief current surges, while fast-acting fuses blow quickly during overcurrent events.
Fuses come in various sizes and shapes, depending on their intended application. Familiarize yourself with the different fuse designs to identify the most suitable option for your needs.
Fuses are sensitive to temperature, which can impact their performance. Ensure your chosen fuse is compatible with the operating temperature range of your application.
Some fuses, like PTCs (Positive Temperature Coefficient), are resettable and can be reused after cooling down. Non-resettable fuses, however, must be replaced once blown.
Fuses use various materials like copper, zinc, and aluminum as their conductive element.
The chosen material can influence a fuse's performance and durability.
Various Types of Fuses play a vital role in protecting our electrical devices and circuits. They serve as the first line of defense against overcurrents, preventing potential damage or even catastrophic failures. By melting under excessive current, fuses effectively break the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity and safeguarding sensitive components.
It's important to select the appropriate fuse for your application because it ensures that safety and functionality are balanced properly. Normal operation is enabled by a well-chosen fuse. Additionally, it offers sufficient defense against surges, short circuits, and electrical faults.
Fuses, in addition to providing safety, also help to save money. Fuse use can ultimately save time and money by reducing repair or replacement costs by avoiding damage to costly equipment and components.
Fuses play a vital role in various applications by protecting devices from electrical hazards. Some of the common uses of fuses, highlighting their importance in everyday life are as follows:

Home Appliances
Fuses safeguard household appliances like TVs, refrigerators, and washing machines from electrical faults, ensuring their longevity and safe operation.
Automotive Industry
Cars utilize fuses to protect their electrical systems and components, such as lighting, audio systems, and engine management systems, from overcurrent events.
Industrial Equipment
Fuses are essential in industrial settings to shield machinery and control systems from electrical damage, ensuring smooth operations and minimizing downtime.
Power Distribution Networks
Fuses help maintain the stability of power distribution networks by interrupting fault currents, protecting transformers, and preventing equipment damage.
Electronics
Small electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops, rely on fuses to protect their delicate components from electrical overloads, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Renewable Energy Systems
Solar panels and wind turbines use fuses to prevent damage from overcurrents, safeguarding these valuable resources and promoting green energy.
Electrical Safety Devices
Fuses are integral components in electrical safety devices like surge protectors and circuit breakers, offering an extra layer of protection against electrical hazards.
Medical Equipment
Fuses are crucial in protecting sensitive medical devices, such as MRI machines and patient monitors, ensuring their safe and reliable operation.
Lighting Systems
Fuses protect lighting systems, including streetlights and home lighting, from overcurrents, helping to maintain a safe and well-lit environment.
HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems utilize fuses to protect their components from electrical damage, ensuring efficient temperature control.
Generally, the fuse is distinguished by its ratings and designs. This represents the highest current, measured in amps, that the fuse can handle before blowing.
When choosing a new fuse, it's crucial to pick one with a suitable power rating. It must respond to current surges fast enough to prevent damage or fires. The fuse's current rating should be slightly higher than the device's normal operating current. This ensures the fuse won't blow and trip the circuit during a minor, harmless surge.
Select NextPCB for top-notch, dependable PCB production and assembly. Begin your journey today and enhance your projects with the professional services of NextPCB. Reach out to us today for more information and a personalized quote. Don't miss the opportunity to take your projects further with our expert services. Contact us now!
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now